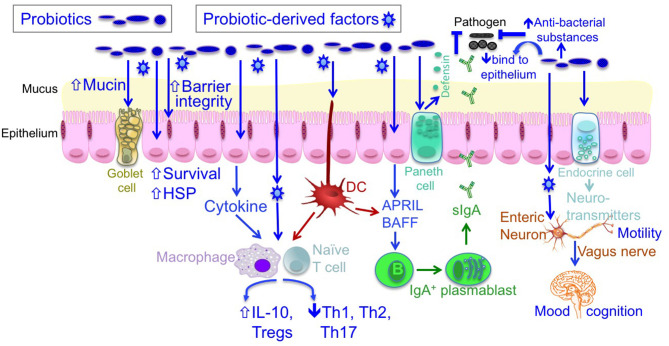
Figure 1.
The mechanisms of probiotic action. Probiotics contribute to maintaining homeostasis and prevention and/or treatment of diseases in host, including (1) blocking pathogenic bacterial effects by producing antibacterial substances and competing with pathogens for binding to epithelial cells; (2) promoting intestinal epithelial cell homeostasis by increasing barrier function, mucus production, survival, and cytoprotective responses; (3) defining the balance between necessary and excessive defense immunity by increasing innate immunity, such as production of IgA and defensin, up-regulating anti-inflammatory cytokine production, and inhibiting proinflammatory cytokine production; and (4) regulating the gut-brain axis through production of neurotransmitters and through the vagus nerve. DC, dendritic cell; IL, interleukin; HSP, heat shock protein.