Figure 7.
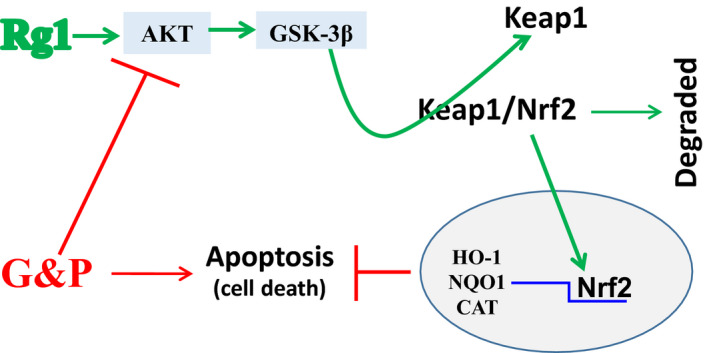
Schematic illustration of the mechanism by which Rg1 protects against G&P‐induced H9C2 injury. G&P could inhibit AKT/GSK‐3β pathway and induce H9C2 cell death, whereas Rg1 could activate AKT/GSK‐3β pathway by phosphorylation, which in turn dissociates Nrf2 from KEAP1 (Kelch‐like ECH‐associated protein 1), transposes into the nucleus, and recognizes the appropriate antioxidant response element (ARE) sequence. As a result, it initiates the transcription of a series of antioxidative genes harboring ARE in the promoter region, including HO‐1, NQO1 and CAT. These antioxidant products protect cells against oxidative stress‐induced apoptosis
