FIGURE 6.
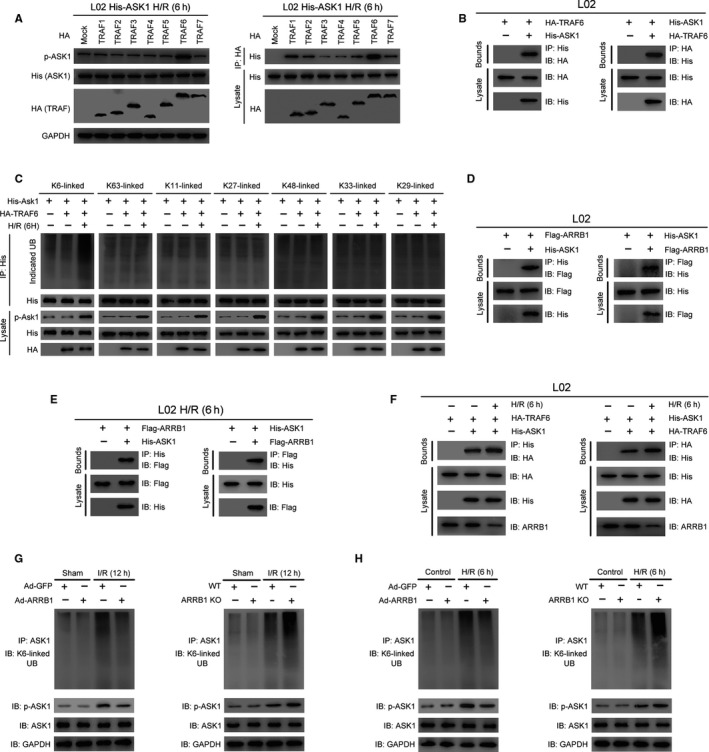
ARRB1 interacts with ASK1 and then antagonizes its TRAF6‐mediated K6‐linked polyubiquitination, thus inhibiting its activation in hepatocytes during hepatic I/R injury. A, Immunoblotting detection of phosphorylated ASK1 protein (left panel) and co‐IP assay for the interaction between His‐ASK1 and HA‐TRAF proteins (right panel) in L02 hepatocytes stimulated with H/R for 6 h. B, His‐tagged ASK1 and HA‐tagged TRAF6 plasmids were cotransfected into L02 hepatocytes. Anti‐His antibody (left panel) and anti‐HA antibody (right panel) were used for immunoprecipitation. C, Immunoprecipitation analysis of indicated ubiquitination types of ASK1 in L02 hepatocytes transfected with HA‐TRAF6 or empty vector in respond to H/R insult or not. D, IP analysis was conducted to detect the binding association between ASK1 and ARRB1 in L02 hepatocytes under normal condition. His‐tagged ASK1 and Flag‐tagged ARRB1 plasmids were cotransfected into L02 hepatocytes. Anti‐His antibody (left panel) and anti‐Flag antibody (right panel) were used for immunoprecipitation. E, IP analysis was conducted to detect the binding association between ASK1 and ARRB1 in L02 hepatocytes when treated with H/R challenge. Anti‐His antibody (left panel) and anti‐Flag antibody (right panel) were used for immunoprecipitation. F, IP analysis showing the expression level of ARRB1 and binding capability between ASK1 and TRAF6 in L02 hepatocytes under H/R challenge or not. Anti‐His antibody (left panel) and anti‐HA antibody (right panel) were used for immunoprecipitation. G and H, Lysates of liver lobes challenged with or without I/R surgery (G) or whole‐cell lysates of primary hepatocytes subjected to or not H/R insult (H) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti‐ASK1 antibody followed by immunoblotting with anti‐K6‐linked polyubiquitination antibody when ARRB1 was overexpressed or knockout
