Fig. 85.3.
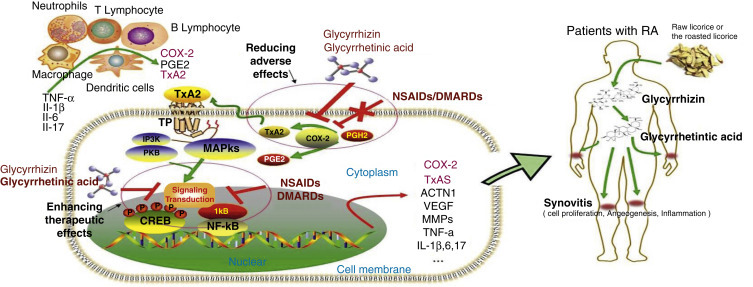
The COX-2/TxA2 pathway is a crucial mechanism underlying the toxicity reducing and efficacy enhancing effects of glycyrrhizin (GL) and glycyrrhetinic acid (GA) to NSAIDs/DMARDs. TNF, Tumor necrosis factor; IL, interleukin; RA FLS, rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes; COX, cyclooxygenase; TxA2, thromboxane A2; TP, thromboxane A2 receptor; PGH2, prostaglandin H2; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; NSAIDs, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; DMARDs, disease modifying antirheumatic drugs; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein; MAPKs, mitogen activated protein kinases; PI3K, phosphoinositide-3-kinase; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; ACTN1, α-actinin-1; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinase.
From Huang QC, Wang MJ, Chen XM, et al. Can active components of licorice, glycyrrhizin and glycyrrhetinic acid, lick rheumatoid arthritis? Oncotarget. 2016;7[2]:1193-1202. PubMed PMID: 26498361.
