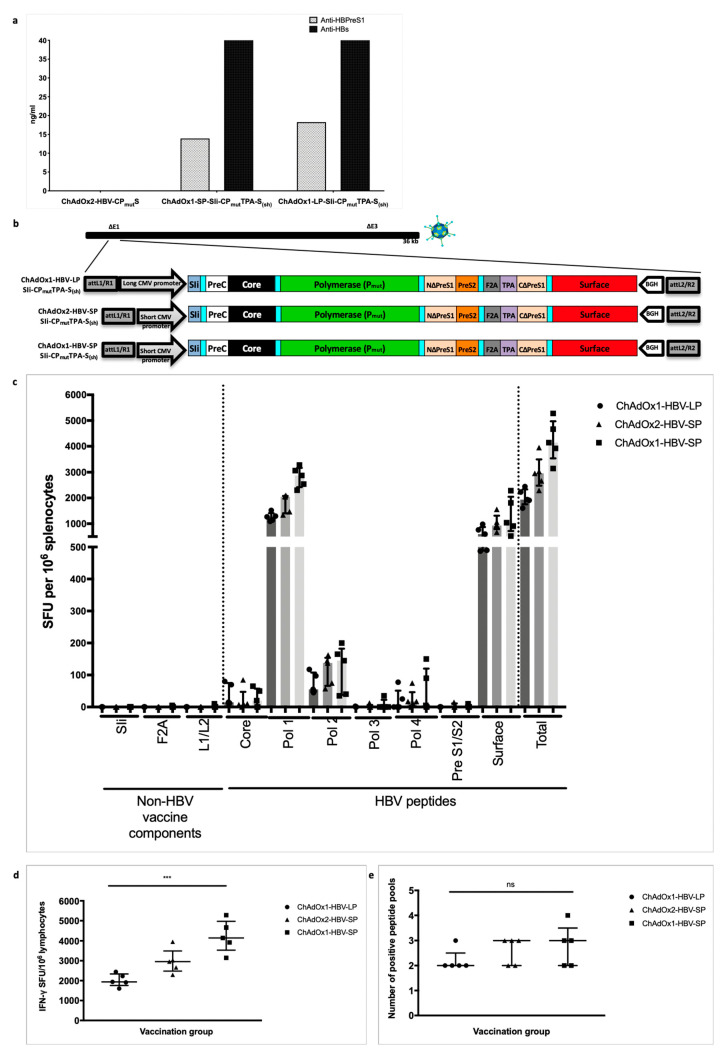
Figure 4.
Second-generation HBV immunogen SIi-CPmutTPA-S(sh) design and immunogenicity of chimpanzee adenovirus (ChAd) vaccine candidates in inbred Balb/c mice. Supernatants from chimp-adenoviral HBV vaccine infected HEK293A cells were harvested 24 h post-infection and quantified in PreS1 and HBs antigen capture ELISA. PreS1 and S antigen quantities based on commercial standard recombinant HBV surface antigen (PIP002, Biorad) obtained from different chimp-adenoviral HBV vaccines, above background value are shown (a). Long-CMV promoter (LP) or short-CMV promoter (SP) based mammalian expression cassettes, encoding SIi-CPmutTPA-S(sh) immunogen were inserted into E1 locus of replication deficient ChAdOx1 or ChAdOx2 vector and four recombinant ChAdOx1-LP-SIi-CPmutTPA-S(sh), ChAdOx1-SP-SIi-CPmutTPA-S(sh), ChAdOx2-LP-SIi-CPmutTPA-S(sh) and ChAdOx2-SP-SIi-CPmutTPA-S(sh) viruses were generated in T-REx™-293 cells (b). Subsequently, all four recombinant viruses were screened by PCR, for stability analysis. Except ChAdOx2-LP-SIi-CPmutTPA-S(sh), other three viruses showed positive PCR result for the presence of an intact HBV-immunogen cassette. BALB/c mice were vaccinated intramuscularly with 5 × 107 infectious units of ChAdOx1-LP-SIi-CPmutTPA-S(sh), or ChAdOx1-SP-SIi-CPmutTPA-S(sh) or ChAdOx2-SP-SIi-CPmutTPA-S(sh) (n = 5 per group). Splenocytes were extracted 14 days after vaccination and plated in IFNγ ELISpot assays with pools of overlapping peptides corresponding to the vaccine immunogen (c). T cell response magnitude was measured by the number of IFNγ SFU per million lymphocytes (d) and breath was measured by the number of positive peptide pools (e) over 100 IFNγ SFU/million cells defined as positive). Median and interquartile ranges are shown. Kruskal–Wallis tests were used for statistical comparison of the three vaccine groups. *** p < 0.001, ns = not significant.