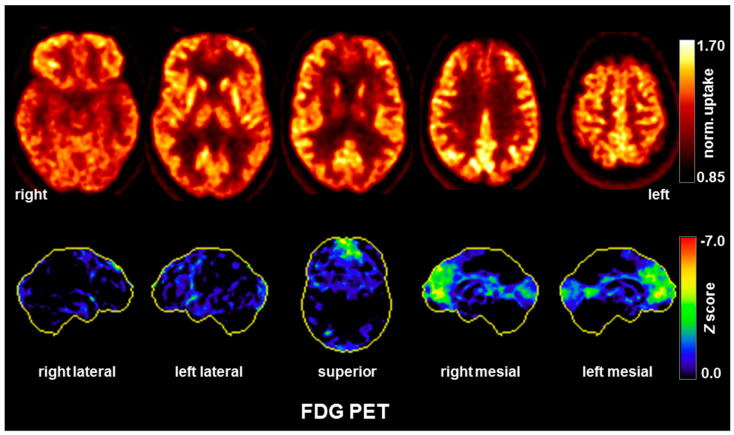
Figure 3.
A [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) examination revealed moderate hypometabolism of the bilateral mesial to medial frontal cortices. Upper row: transaxial FDG-PET images (voxel-wise FDG uptake normalized to whole brain uptake); lower row: 3D surface projections of regions with decreased FDG uptake (color-coded Z-score, compared to age-matched healthy controls; minor, linear-shaped areas of mild hypometabolism were judged to be non-specific partial volume effects due to atrophy, whereas occipital cortex hypometabolism was probably caused by closing the eyes; [17]). The FDG-PET of the brain was performed 50 min after injection of 214 MBq FDG (Vereos Digital PET/CT, Philips Healthcare, The Netherlands). Abbreviations: R, right; l, left.