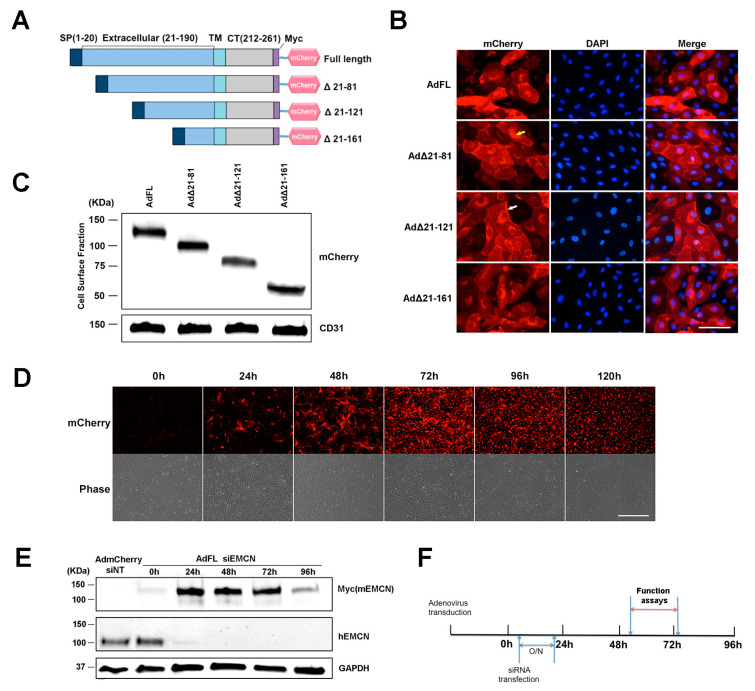
Figure 1.
Endomucin (EMCN) mutants: constructs, expression, and experimental design. (A) Schematic representation of the full-length (FL) murine EMCN protein and the truncation mutants. SP, signal peptide; TM, transmembrane domain; CT, cytoplasmic tail; mCherry, fluorescence tag. (B) Human retinal endothelial cells (HRECs) were transduced overnight with adenoviruses expressing EMCN-truncated mutants. Autofluorescence of mCherry was examined 48 h post-infection. Scale bar: 100 um. Expression of all of the constructs was detected in the cytoplasm (indicated by yellow arrow) as well as on the cell surface (indicated by white arrow). (C) Adenoviruses expressing EMCN-truncated mutants were transduced into HRECs, and cell surface proteins were labeled by biotinylation and analyzed by western blot using antibodies against mCherry and CD31. The FL as well as all of the mutants were detected at the cell surface at the expected molecular weights. (D) HRECs were transduced with adenoviruses expressing EMCN truncated overnight, and mCherry fluorescence and phase contrast was examined every 24 h. Scale bar: 200 μm Expression was detected as early as 24 h, peaked at 72 h, and declined thereafter. (E) Cells lysates of HRECs in which endogenous hEMCN had been knocked down using siRNA and overexpressing full-length mouse EMCN was collected every 24 h. and protein levels of Myc-tagged (Myc mEMCN) and hEMCN were examined by western blot. GAPDH was used as loading control. Endogenous hEMCN was effectively knocked down at 24–96 h whereas exogenously expressed mEMCN was highly expressed at 24–72 h. (F) Experimental design for subsequent studies shows that HRECs were transduced with adenoviruses overexpressing mEMCN mutants, and one day later, endogenous hEMCN was knocked down using siRNA. In vitro functional assays, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) internalization and co-IP were conducted 48–72 h post-transfection.