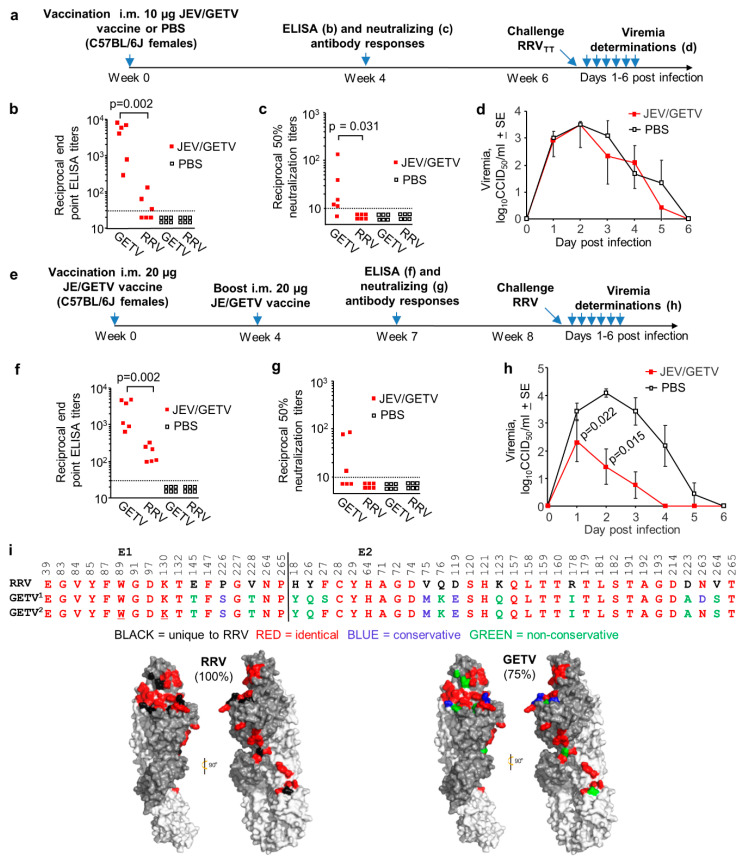
Figure 5.
Cross-protection against RRV mediated by the Japanese Encephalitis (JEV)/ Getah virus (GETV) vaccine. (a) Timeline of the single 10 µg vaccination with JEV/GETV vaccine (the GETV vaccine strain is MI-110) or PBS, antibody measurements and RRVTT challenge; (b) GETVMM2021 and RRVTT endpoint IgG ELISA titers after 1 vaccination with JEV/GETV vaccine or PBS (limit of detection 1 in 30); (c) GETVMM2021 and RRVTT 50% neutralization titers after 1 vaccination with JEV/GETV vaccine or PBS (limit of detection 1 in 10); (d) RRVTT viremia post-challenge with RRVTT in mice vaccinated once with JEV/GETV vaccine or PBS (n = 6 mice per group). (Limit of detection for each mouse 2 log10CCID50/mL.); (e) Timeline of two 20 µg vaccinations with JEV/GETV vaccine or PBS, antibody measurements and RRVTT challenge; (f) GETV and RRVTT endpoint IgG ELISA titers after 2 vaccinations with JEV/GETV or PBS (limit of detection 1 in 30); (g) GETVMM2021 and RRVTT 50% neutralization titers after 2 vaccinations with JEV/GETV vaccine or PBS (limit of detection 1 in 10); (h) RRVTT viremia post-challenge with RRVTT in mice vaccinated twice with JEV/GETV vaccine or PBS (n = 6 mice per group). Statistics by Kolmogorov–Smirnov tests; (i) As for Figure 3a,b the 48 E1/E2-MXRA8 contact residues (based on CHIKV) are aligned for RRVTT and GETVMI-110 (GETV1, vaccine strain) and GETVMM2021 (GETV2) E1/E2, with GETVMI-110 residues colored in the cryo-EM structures of E1/E2. GETVMI-110 shows 75% amino acid identity in these 48 amino acids with RRVTT. The conserved, but formalin-fixation-sensitive, amino acids K and W are underlined.