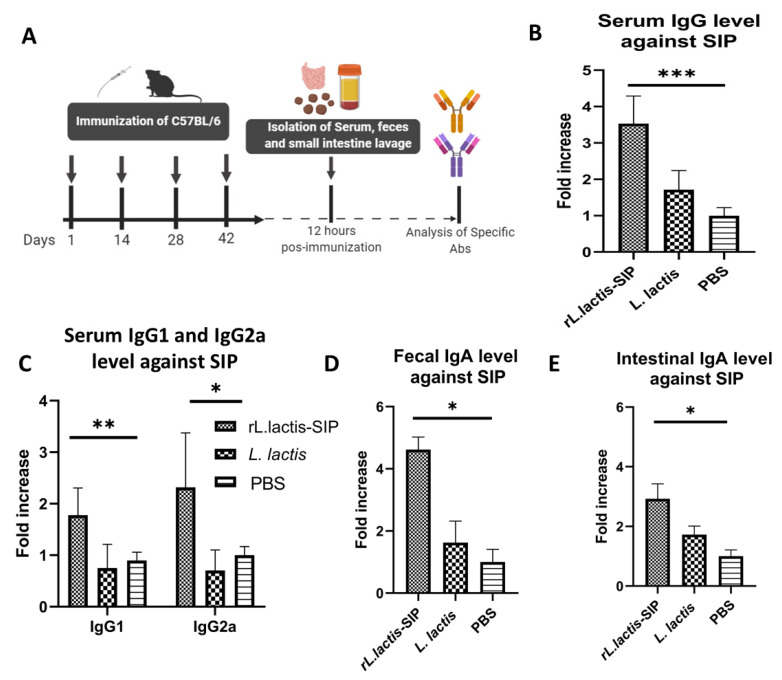
Figure 2.
Oral immunization induced with rL. lactis-SIP generated systemic and mucosal anti-SIP immunoglobulin G (IgG) and immunoglobulin A (IgA). (A) Representation of the immunization used in C57BL/6 mice experiment. The mice (per group) were orally immunized four times with 1 × 1010 CFU of rL. lactis-SIP at intervals of 14 days. The mice in the control groups were immunized with 1 × 1010 CFU of L. lactis or PBS. The secretion of specific immunoglobulins against SIP was measured by ELISA from the sera collected from mice immunized without GBS colonization. Serum anti-SIP: (B) IgG, (C) IgG1 and IgG2a, (D) IgA from feces, and (E) intestinal IgA production were determined with respect to the PBS-immunized mice (control). Results represent one of two independent experiments with similar results. The bars indicate the mean ± standard deviation of immunoglobulins. *** p < 0.0001; ** p < 0.001; * p < 0.05 by multiple-comparison ANOVA for rL. lactis-SIP immunized mice compared with PBS-immunized mice.