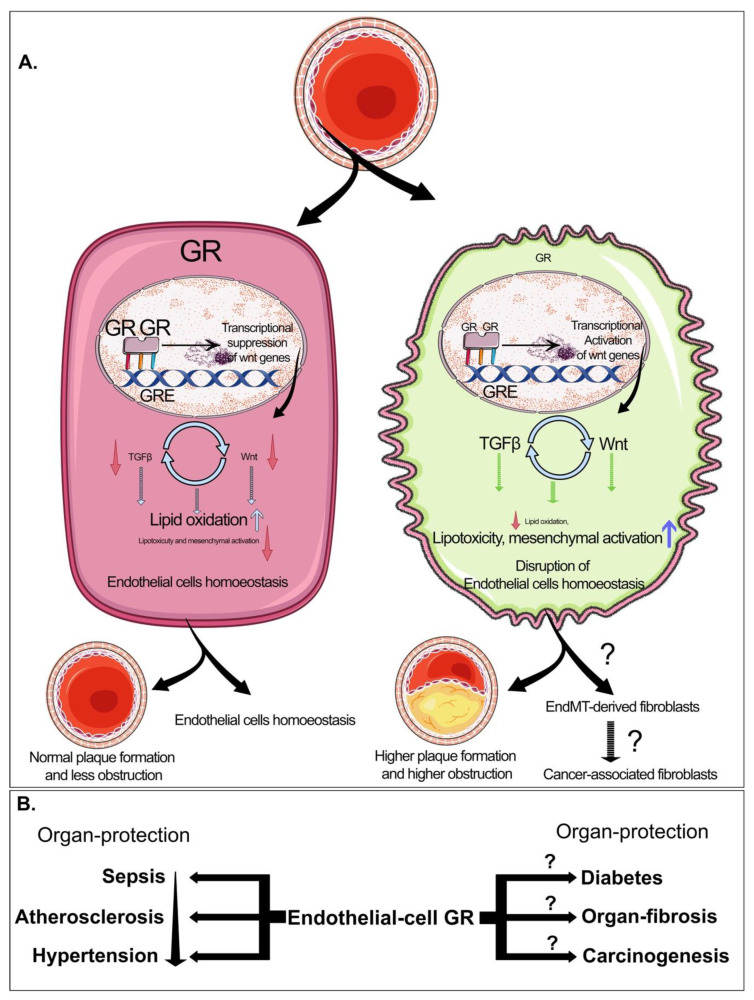
Figure 4.
Functional significance of glucocorticoid receptor in endothelial cells. (A). In normal endothelial cells, in the presence of GCs, GR binds to GREs and activates the transcription and trans-repression of genes responsible for canonical Wnt signaling. Suppressed Wnt/TGF-β signaling leads to lipid homeostasis and low levels of EndMT, therefore contributing to endothelial cell homeostasis. In diabetic endothelial cells, GR level is suppressed, leading to transcriptional activation of genes in the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Higher levels of Wnt-dependent TGF-β signaling lead to disruption in lipid homeostasis and higher levels of EndMT, thereby disrupting endothelial cell homeostasis. (B). Flowchart showing the role of endothelial cell GR in organ protection.