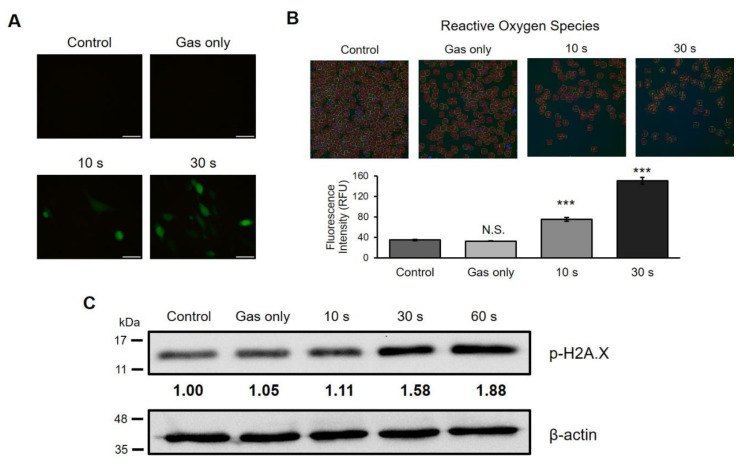
Figure 3.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and DNA damage after exposure to cold atmospheric plasma (CAP). (A) Representative images of the canine osteosarcoma D-17 cell line after exposure to CAP at the indicated time. CAP-treated cells were stained with H2DCFDA and photographed under a fluorescence microscope. H2DCFDA is converted to DCF by ROS. DCF, 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein. Scale bars, 50 μm. (B) Quantitative analysis of ROS using high-content screening. CAP-treated D-17 cells stained with H2DCFDA and Hoechst 33342 were measured by high-content screening technology. Error bars represent the mean ± S.E.M. of three replicates. Magnification, 100X. (C) Western blot analysis of DNA damage. Expression of phospho-histone-H2A.X was measured to assess DNA damage. This result represents two independent experiments. The intensity was normalized to β-actin. *** p < 0.001; N.S. indicates not significant.