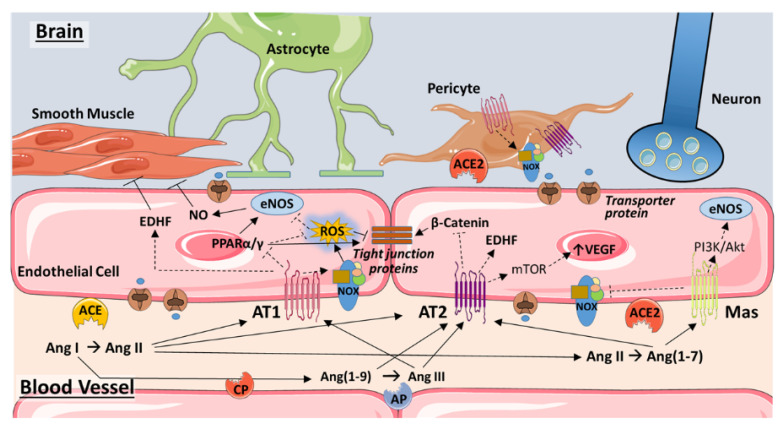
Figure 2.
Angiotensin signaling in the endothelium of the blood–brain barrier. Traditional and novel components of the renin–angiotensin system (RAS) converge at the level of the endothelium to modulate blood flow, vascular remodeling, and brain permeability. Ang II formed by the actions of ACE on Ang I may act on the AT1 receptor to induce either vasodilation, via production of EDHF, or vasoconstriction by stimulating ROS production via Nox2 and attenuating eNOS-induced NO production. Inhibition of PPARα/γ may exacerbate ROS production. Ang II-induced ROS and inhibition of PPARα/γ may act synergistically to increase blood–brain barrier permeability by impeding the expression or functioning of tight junction proteins. ROS contributes as well to adverse vascular remodeling and vessel rarefaction that impedes blood flow and occurs with hypertension and aging. Through AT2R, Ang II may induce vasodilation via EDHF production. AT2R is also linked to cardioprotective effects via vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression, as well as strengthening of interendothelial junctions via inhibition of β-catenin. However, VEGF is also implicated in the disruption of the blood–brain barrier. NO may also increase AT2R expression, which in turn may reduce ACE levels (not shown). Ang(1–9), Ang(1–7), and Ang III may activate AT2R as well, with Ang III also acting on AT1R. Ang(1–7), formed from Ang II by ACE2, acts upon the Mas receptor to constitute a protective arm of RAS through inhibition of Nox2 and activation of eNOS. In pericytes, AT1R activation may induce oxidative stress by increasing Nox4, thereby triggering pericyte loss and compromising the blood–brain barrier. Based on recent research in the heart, brain pericytes may also express ACE2. Not shown are the RAS components associated with astrocytes and neurons. See text for additional details. Abbreviations: ACE, angiotensin converting enzyme; AP, aminopeptidase; AT1, angiotensin II type 1 receptor; AT2, angiotensin II type 2 receptor; CP, carboxypeptidase; EDHF, endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NO, nitric oxide; NOX, NADPH oxidase; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PPARα/γ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha/gamma; ROS, reactive oxygen species; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor. Some images are from Servier Medical Art (https://smart.servier.com/).