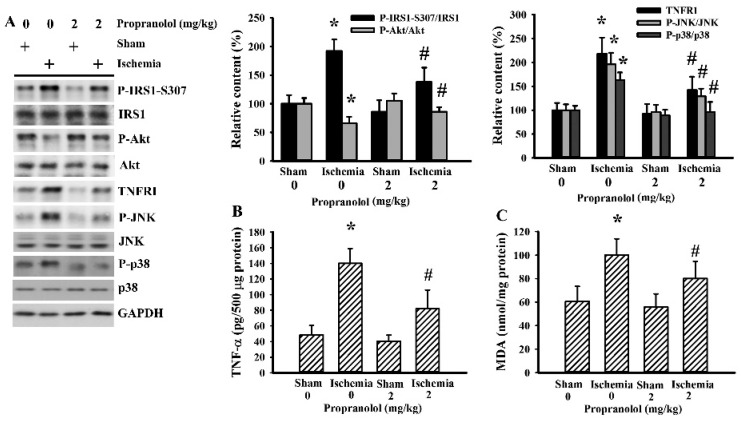
Figure 7.
Propranolol alleviated postischemic gastrocnemius inflammation. Rats receiving a normal saline vehicle or a propranolol (2 mg/kg) intraperitoneal injection were subjected to sham and permanent cerebral ischemia for 24 h. (A) Proteins were extracted from the gastrocnemius muscles and subjected to Western blot with the indicated antibodies. (B) Proteins were extracted from the gastrocnemius muscles and subjected to ELISA for the measurement of TNF-α. (C) The contents of MDA in the gastrocnemius muscles were measured. * p < 0.05 vs. the sham/saline group and # p < 0.05 vs. the ischemia/saline group, n = 6.