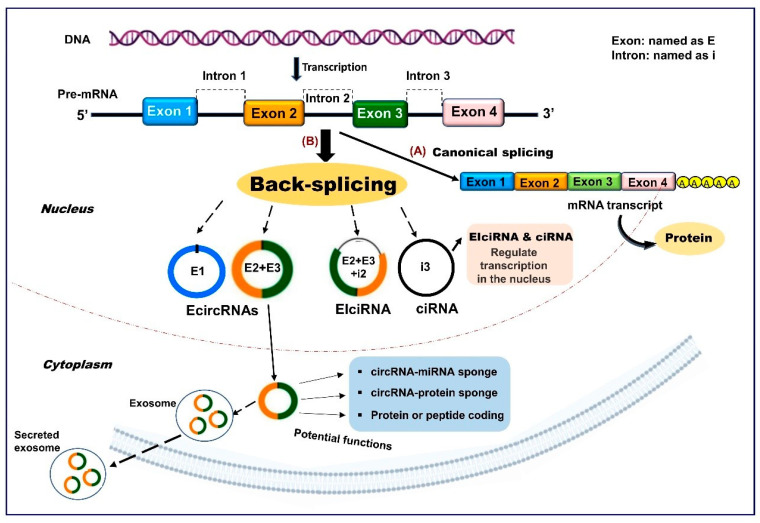
Figure 1.
A simplified schematic representation of circular RNAs (circRNAs) biogenesis. (A) Pre-mRNA can undergo canonical splicing to generate a linear mRNA transcript that is subsequently translated into protein. (B) Pre-mRNA can also be spliced in the noncanonical manner “back-splicing”, wherein a downstream splice donor site is joined to an upstream splice acceptor site to produce circular RNA molecules. Three different types of circRNAs can arise from different genomic positions and combinations, including: (1) exonic circRNAs (EcircRNAs), (2) exon-intron circRNAs (EIciRNAs), and (3) circular intronic RNAs (ciRNAs). The formation mechanisms and potential functions of these circRNA types are discussed in the text.