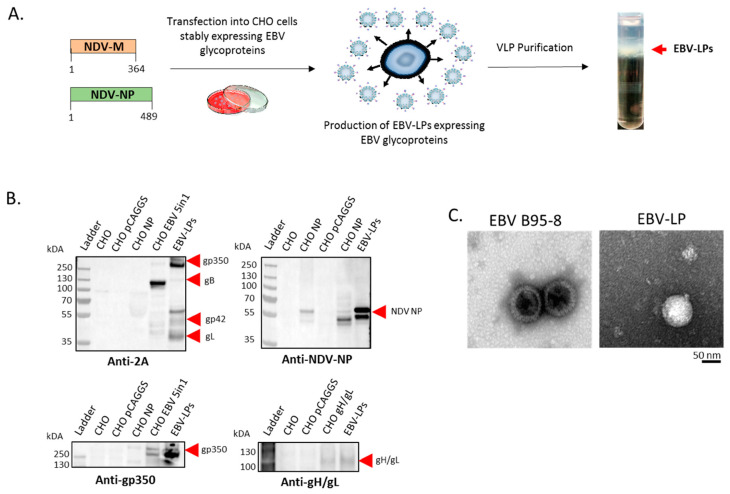
Figure 2.
Production and characterization of EBV-like particles (EBV-LPs). (a) Generation of EBV-LPs in CHO cells stably expressing five EBV glycoproteins. CHO cells stably expressing the five glycoproteins were co-transfected with plasmids encoding NDV-M and NDV-NP proteins (amino acid numbers in each of the NDV proteins are shown) to induce production of EBV-LPs. After transfection, supernatants were collected between 24–120 h post-transfection and EBV-LPs were pelleted by ultracentrifugation and purified through a sucrose density gradient (EBV-LP layer shown by red arrow); (b) Immunoblot analysis of purified EBV-LPs. After lysis, purified EBV-LPs were resolved on a 4–12% polyacrylamide gel, transferred to a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane, and analyzed by immunoblot with anti-2A polyclonal, anti-NDV-NP polyclonal, anti-gp350 monoclonal (72A1), and anti-gH/gL polyclonal primary antibodies, as indicated. Untransfected CHO cells (CHO), CHO cells transfected with “empty” pCAGGS vector (CHO pCAGGS), CHO cells transfected with pCAGGS-NDV-NP vector alone (CHO NP), CHO cells transfected with pCAGGS-gH/gL-WT (CHO gH/gL), and stable CHO cells expressing EBV gp35-F-gB-F-gp42-gL-gH-F (CHO EBV 5in1) served as controls when indicated; (c) TEM analysis of purified EBV-LPs. Purified EBV virions and EBV-LPs were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and adsorbed to glow-discharged, carbon-coated, 200-mesh EM grids. Micrographs were collected using an FEI Tecnai 12 TEM and recorded with a Gatan 2 × 2 k CCD camera at a magnification of 21,000X and a defocus value of ∼1.5 μm.