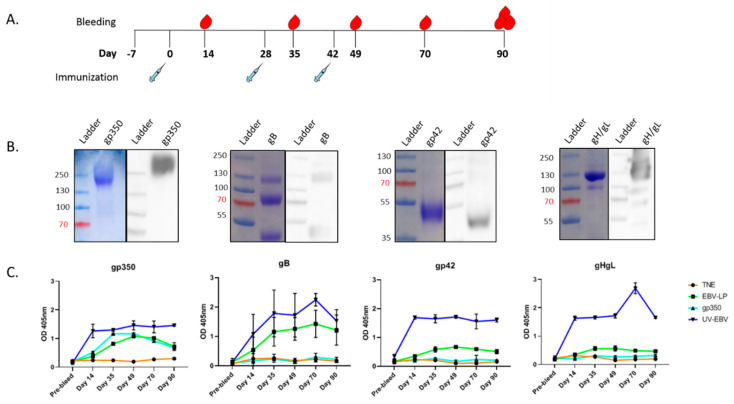
Figure 3.
Antibody response in EBV-LP-immunized New Zealand white rabbits. (a) New Zealand white rabbit immunization and bleeding schedule schematic. Rabbits were immunized and bled as detailed in the Materials and Methods; (b) Biochemical characterization of recombinant EBV proteins used as ELISA target antigens. Coomassie stain (left) and immunoblot (right; performed using anti-6×His primary antibody) of soluble gp350 ectodomain, and recombinant EBV gB, gp42, and gH/gL proteins, which were used as target antigens in ELISA assay in panel C; (c) EBV-specific antibody responses in sera. IgG titers in immunized animals were measured by ELISA for each glycoprotein; proteins described in panel B were used as target antigens at 25 ng/well, and sera from immunized rabbits for each treatment group and timepoint were pooled, serially diluted, and used as primary antibody (1:100 dilution shown). Primary mouse mAbs anti-gp350 (72A1), anti-gB (CL55), anti-gp42 (F-2-1), anti-gL (E1D1), and anti-gH/gL (CL59) were used as positive controls where appropriate (not shown). Antibody binding was detected with HRP-labeled anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody, and optical density (OD) was read at 405 nm with a spectrophotometer. ELISA assay was performed for each sample in quadruplicate, and results are expressed as mean ± standard deviations (SD). The assay was independently repeated two times with either individual animal serum or pooled sera.