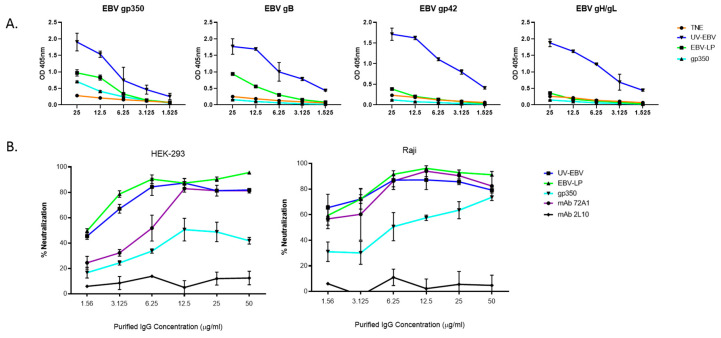
Figure 4.
In vitro neutralizing activity of purified IgGs from rabbits immunized with EBV-LPs. (a) Titration of purified Day 70 IgGs specific to EBV. Equal amounts of Day 70 sera from immunized rabbits from each treatment group (UV-EBV, EBV-LP, gp350, and TNE) were pooled, and total IgG antibodies were purified via protein A spin columns. Total IgGs were serially diluted (25, 12.5, 6.25, 3.125, and 1.56 µg/mL) and EBV-glycoprotein-specific IgG titers were determined in each dilution in quadruplicate by ELISA as described in Figure 3C. Results are expressed as mean ± SD; (b) EBV-eGFP neutralization assay in Raji B cells and HEK-293 epithelial cells. Neutralization activity of purified Day 70 IgGs was determined by incubating known quantities of EBV-eGFP that result in 40–70% infectivity with serially diluted purified IgGs (50, 25, 12.5, 6.25, 3.125, and 1.56 µg/mL µg/mL) from all treatment groups for 1 h at 37 °C. The mixtures of purified IgGs and virus were then added to previously seeded cells and incubated for 2 h at 37 °C, after which the cells were thoroughly washed three times with 1×PBS and given complete media. Cells were collected after 48 h and infected cells (eGFP-positive) were quantified using FACS. Cells incubated with virus or media alone served as positive and negative controls for infection, respectively, and resulting infectivity was used to calculate % neutralization. Neutralizing anti-gp350 mAb 72A1 and non-neutralizing anti-gp350 mAb 2L10 served as positive and negative controls for neutralization, respectively. Results were normalized to the TNE group and are shown as mean ± SD.