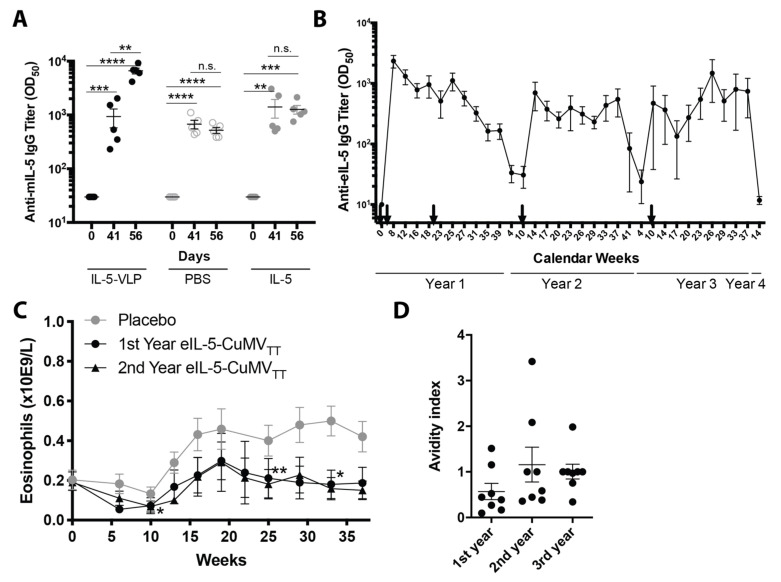
Figure 2.
Longitudinal IL-5-specific IgG antibody titer including neutralization and avidity without self-induction. (A) Endogenous self-induction. IL-5-specific IgG antibody titers were measured in serum by the ELISA of mice following vaccination with mIL-5-VLP applied on days 0, 14, and 28 and an endogenous-mimicry challenge with either mIL-5-VLP (filled black), PBS (open), or mIL-5 alone (filled grey), applied on day 42. Individual antibody titers are per group (n = 5) with mean and SEM. Significances were obtained by a 2-way ANOVA; multiple comparisons with paired t-tests are at different time points within groups. (B) Longitudinal anti-IL-5 IgG. Antibody titer reversibility shown by the course of IL-5-specific antibody titers in horses of a 3-year clinical study; IL-5-specific IgG antibody titers (mean +/− SEM) were measured in the serum of horses over three years at different time points. Arrows indicate vaccine injections. The graph contains parts of data of Figure 1 and Figure 2, of Fettelschoss-Gabriel et al. 2019, Allergy. (C) Course of eosinophils in the blood during three IBH seasons: placebo-treated season (grey circle, n = 13), first year (black circle, n = 13), and second year (black triangle, n = 11) vaccination season. Part of the data of Figure 2c is published in Fettelschoss-Gabriel et al. 2019, Allergy. The mean and SEM are shown, statistical analysis was performed by the Friedman test. (D) Avidity of the IL-5-specific IgG antibodies of eight horses after the yearly booster in the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd year. The avidity index is plotted for individual horses in each year with the mean and SEM; the statistical analysis was performed by the Friedman test (*) followed by a multiple comparison test (n.s.). ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001.