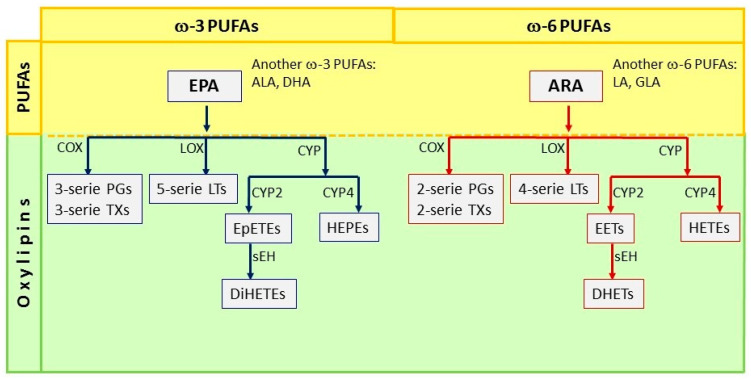
Figure 1.
Pathways of synthesis of oxylipins from Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and ARA PUFAs. ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) include α-linolenic acid (ALA), Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA); the metabolism of EPA by Cyclooxygenase (COX) leads to the formation of 3-series prostaglandins (PGs) and 3-series Thromboxanes (TXs); the Lipoxygenase (LOX) pathway generates 5-series Leukotrienes (LTs); and the cytochrome P450 (CYP2) epoxygenases leads to the formation of Epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (EpETEs). EpETEs are further metabolized by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) to form the fatty acid diols termed Dihydroxy eicosatetraenoic acids (DiHETEs); CYP4 generates hydroxyeicosapentaenoic acids (HEPEs). In contrast, ω-6 PUFAs include linoleic acid (LA), γ-linolenic acid (GLA), and araquidonic acid (ARA). The metabolism of ARA through the COX pathway generates 2-series prostaglandins (PGs) and thromboxanes (TXs), while through the LOX pathway it generates the 4-series leukotrienes; ω-hydroxylase results in the formation of hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HETEs); the activity of the epoxygenase leads to epoxy-eicosatrienoic acids (EETs), which can be converted to dihydroxy eicosatetraenoic acids (DiHETs) by the enzyme epoxy-hydroxylase (sEH).