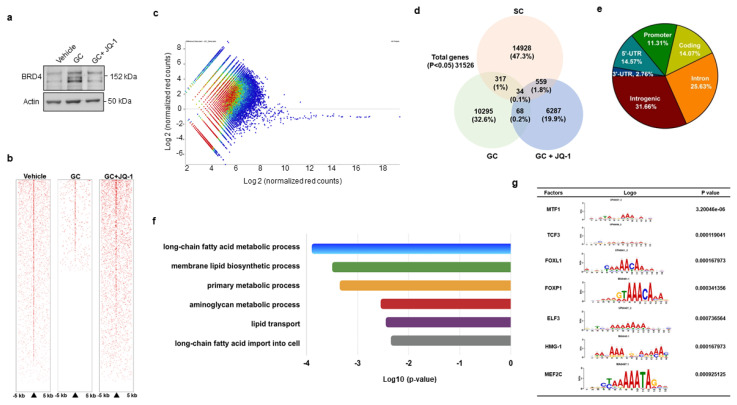
Figure 3.
ChIP-seq analyses of H3K9ac-binding genes in vehicle-, glucocorticoid-, and JQ-1-treated mesenchymal stem cells. JQ-1 treatment attenuated glucocorticoid-induced BRD4 levels (a). Heatmaps of ChIP-seq analyses showing H3K9ac occupancy in DNA within 5 kb upstream and downstream of transcriptional start site (b). Scatter plots of H3K9ac ChIP-seq signals distribution in Veh, GC, GC + JQ-1 groups (c). Venn diagram displaying the overlap of H3K9ac-enriched genes (d). Relative distribution of H3K9ac occupancy across genomic regions (e). Gene set enrichment analysis of H3K9ac marks showed significant changes in fatty acid and lipid metabolism in the Vehicle, GC, and GC + JQ-1 groups (f). The H3K9ac-enriched motif of transcription factors identified in the vehicle, GC, and GC + JQ-1 groups (g). ChIP-seq of H3K9ac-enriched epigenome was performed using Illumina HiSeq4000 system. Experiments were performed three times. Veh: vehicle; GC: glucocorticoid.