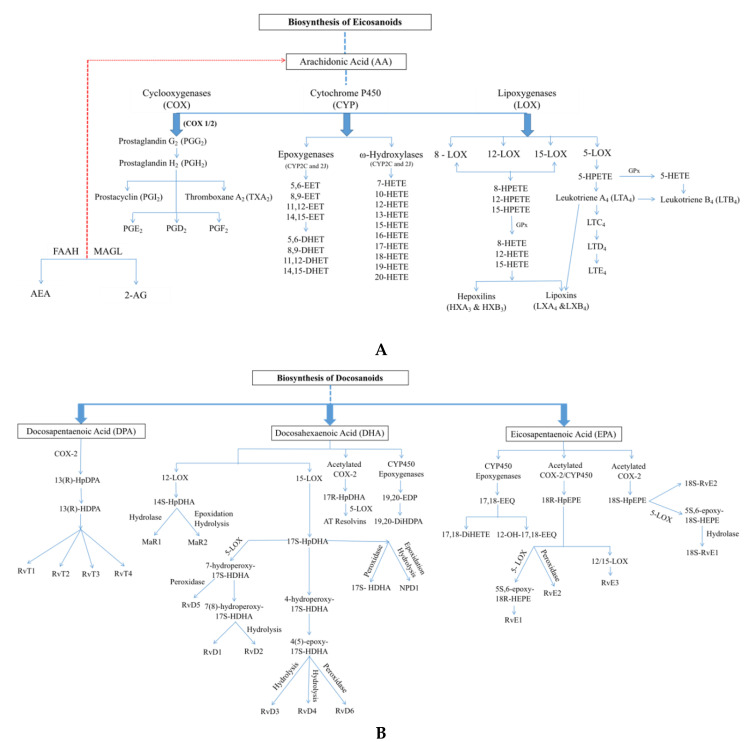
Figure 1.
Biosynthesis of eicosanoids and docosanoids. (A) Eicosanoid biosynthesis starts with the release of arachidonic acid (AA) from membrane phospholipids and is catalyzed by three major enzyme families: cyclooxygenases (COXs), lipoxygenases (LOXs), and cytochrome P450 epoxygenases (CYPs). COXs produce prostaglandins (PGs) and thromboxanes (TXs) through the actions of specific synthases; LOXs produce biologically active metabolites, such as hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HPETEs), hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HETEs), and leukotrienes (LTs), while CYPs metabolize AA into epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids (DHETs), and HETEs. Arachidonic acid can be recycled from the breakdown of endocannabinoids through the actions of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL). (B) Docosanoids originate from eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosapentaenoic acid (DPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which are then converted into a series of lipid mediators, including resolvins, protectins, and maresins. Abbreviations: 2-AG, 2-arachidonoylglycerol; AA, arachidonic acid; AEA, N-arachidonoylethanolamine/anandamide; AT, aspirin-triggered; COX, cyclooxygenase; CYP, cytochrome P450; DHA, docosahexaenoic acid; DHET, dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acid; DiHDPA, dihydroxydocosapentaenoic acid; DiHETE, dihydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid; DPA, docosapentaenoic acid; EDP, epoxydocosapentaenoic acid; EEQ, epoxyeicosatetraenoic acid; EET, epoxyeicosatrienoic acid; EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid; FAAH, fatty acid amide hydrolase; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; HDHA, hydroxydocosahexaenoic acid; HDPA, hydroxydocosapentaenoic acid; HEPE, hydroxyeicosapentaenoic acid; HETE, hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid; HpDHA, hydroperoxydocosahexaenoic acid; HpDPA, hydroperoxydocosapentaenoic acid; HpEPE, hydroperoxyeicosapentaenoic acid; HPETE, hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid; HX, hepoxilin; LOX, lipoxygenase; LT, leukotriene, LX, lipoxin; MAGL, monoacylglycerol lipase; MaR, maresin; NP, neuroprotectin; OH, hydroxyl group; PG, prostaglandin; RV, resolvin; TX, thromboxane.