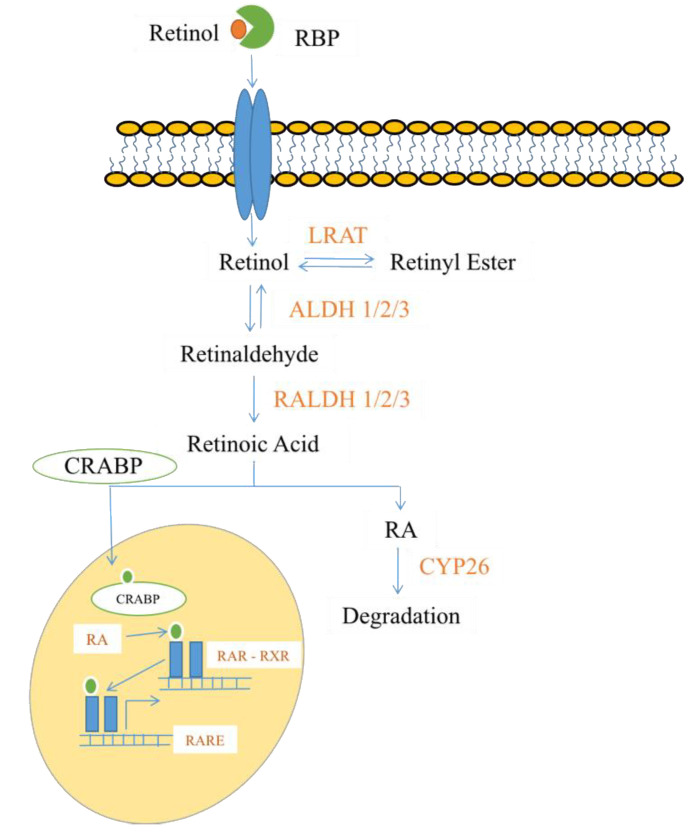
Figure 2.
Mechanism of retinoic acid signaling. Upon reaching its target tissue, retinol is released from RBP and enters cells through specialized receptors. Once inside the cell, retinol can be stored as retinyl esters or irreversibly metabolized to retinoic acid by retinaldehyde dehydrogenase enzymes through a retinaldehyde intermediate. Bioactive RA enters the nucleus bound to CRABP and activates a RAR-RXR heterodimer, leading to transcription of RAREs. When no longer needed, RA is degraded by CYP26 enzymes and cleared from the body. Abbreviations: ALDH, aldehyde dehydrogenase; CRABP, cellular retinoic acid-binding protein; CYP26, family 26 of cytochrome P450 enzymes; LRAT, lecithin retinol acyltransferase; RA, retinoic acid; RALDH, retinaldehyde dehydrogenase; RAR, retinoic acid receptor; RARE, retinoic acid response element; RBP, retinol-binding protein; RXR, retinoid X receptor.