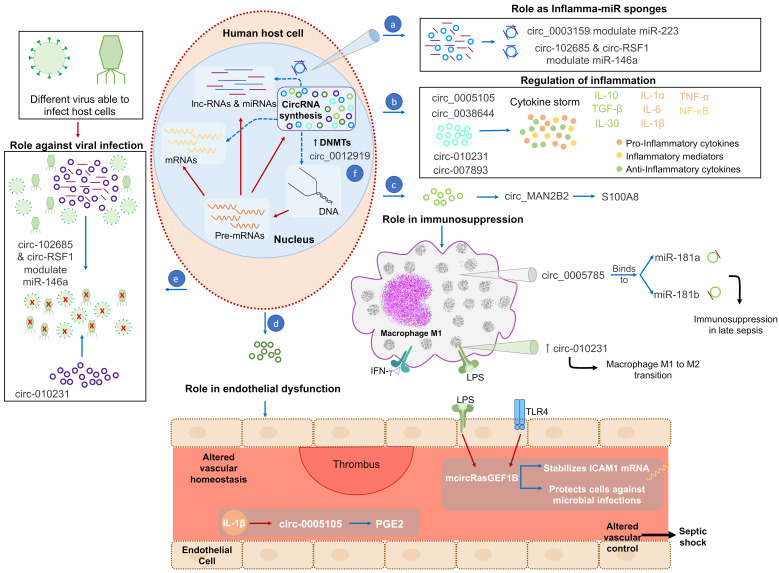
Figure 3.
CircRNAs controlling several molecular mechanisms in sepsis. During sepsis, different molecules induce the activation of circRNAs biogenesis. (a) CircRNAs are able to bind to miRNAs and modulate their expression by inhibiting their functioning. (b) CircRNAs regulate inflammation by controlling the expression of inflammatory mediators and pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines. (c) Immunosuppression is also mediated by circRNAs, for example by mediating the control of immunosuppression mediators such as S100A8, or of macrophages or other immune cells. Notably, when macrophages bind LPS or INFγ, they produce circRNAs, which can act directly or through miRNA binding. (d) CircRNAs during sepsis participate in endothelial dysfunction and alter vascular homeostasis by producing a thrombus. (e) Specific circRNAs compete with viral mRNA to help host defense. (f) Finally, circRNAs have the capacity to increase DNMTs production, thereby altering transcription in immune cells. LPS: lipopolysaccharide; INFγ: interferon gamma; TLRs: toll-like receptors; mRNA: messenger RNA; lnc-RNA: long non-coding RNA; miRNA: microRNA; CircRNAs: circular RNAs; DNMTs: DNA methyl-transferases. Blue arrows indicate the processes activated by circRNA and red arrows denote signaling or activated processes. The red “x” inside viruses indicates virus neutralization.