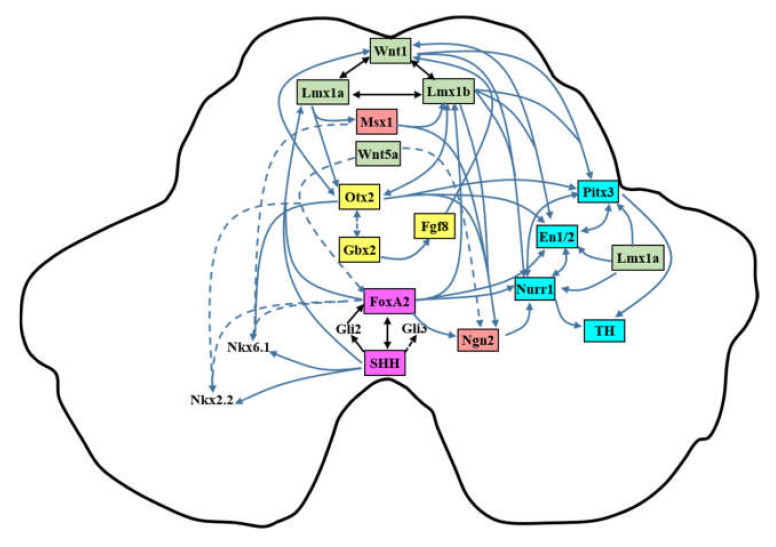
Figure 4.
Genetic regulation of transcription factors in the development of the mDA neurons: The transcription factors are color-coded according to their expressions: purple = floor plate marker, yellow = midbrain–hindbrain boundary (MHB)-related genes, green = roof plate marker, red = neurogenesis marker, and blue = marker of postmitotic mDA neuron. The solid line denotes positive regulation; the dotted line means inhibition. FoxA2 is induced by Sonic hedgehog (SHH) either via SHH itself or its downstream Gli family (SHH-FoxA2 loop). FoxA2 regulates Lmx1a/b and suppress Nkx2.2 and Nkx6.1, while SHH positively regulates Nkx2.2 and Nkx6.1. Otx2 and Gbx2 mutually inhibit each other’s expression. Otx2 inhibits Nkx2.2 but positively regulates Nkx6.1. Gbx2 controls Fgf8 expression, which can regulate Wnt1. Wnt1 interacts with Lmx1a/b, forming a Wnt-Lmx1a/b loop. Lmx1a regulates Msx1 expression, which positively activates Lmx1b and pan-neuronal gene Ngn2 but inhibits Nkx6.1, while Wnt5a is an inhibitor for FoxA2 and Ngn2. FoxA2, Lmx1b, Lmx1a (via Msx1), and Otx2 all positively control Ngn2. Three postmitotic markers, Nurr1, En1, and Pitx3, reciprocally govern each other’s expression. Wnt1-Lmx1a/b, FoxA2 (absent in control of Pitx3), and Otx2 (absent in control of Nurr1) contribute to these three postmitotic markers. Nurr1 and Pitx3 facilitate the induction of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH).