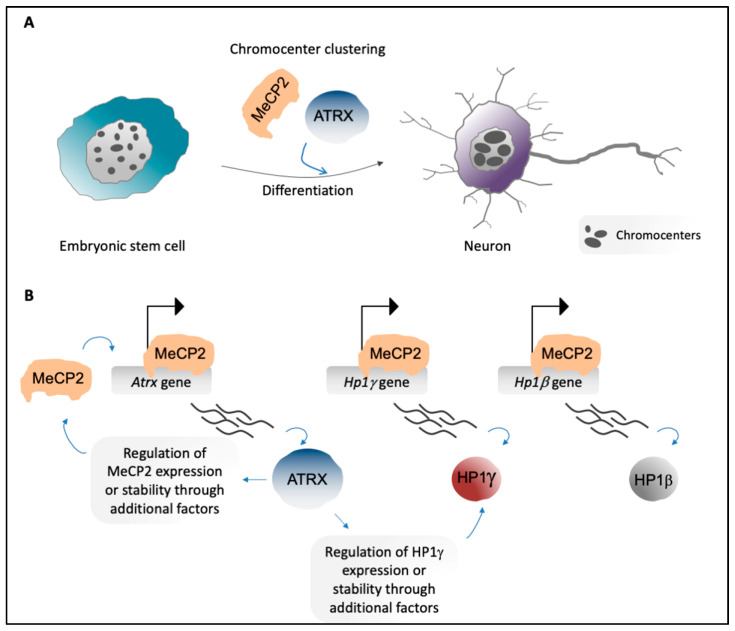
Figure 3.
(A) Embryonic stem cells show high numbers of chromocenters per nucleus (left). In neurons, chromocenters increase in size and decrease in number due to aggregation of PCH of different chromosomes (chromocenter clustering) [18,20] (right). MeCP2 [18] and ATRX [20] are important players in chromocenter clustering during neural differentiation. (B) MeCP2 directly promotes expression of genes that encode PCH-associated factors, including Atrx, Hp1γ, and Hp1β (top). ATRX regulates expression and/or stability of MeCP2 and HP1γ, probably through the involvement of additional factors [20] (bottom).