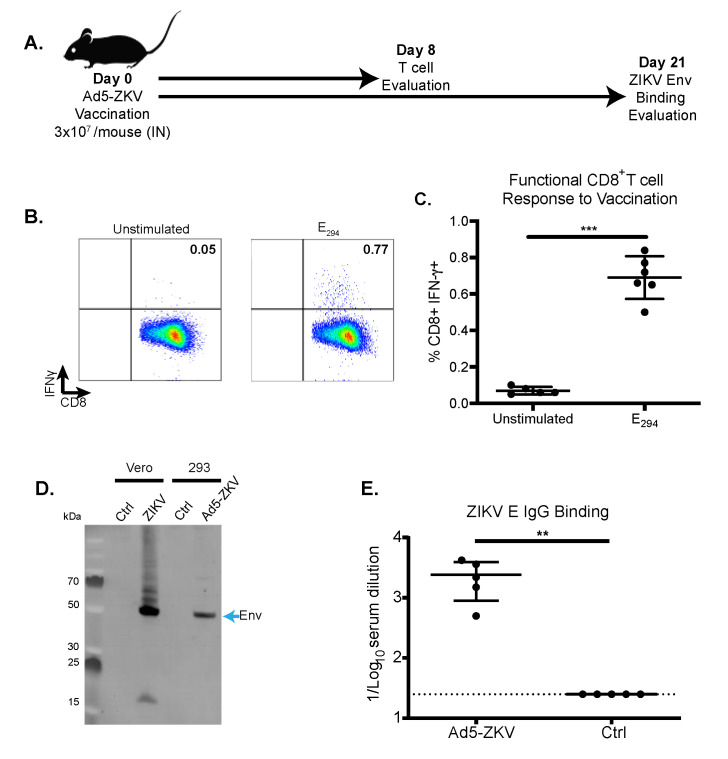
Figure 2.
Immunogenicity of hAd5-ZKV vaccine in wild type C57BL/6 mice. (A) Graphical timeline for hAd5-ZKV vaccination and the evaluation of immunogenicity. C57Bl/6 mice were immunized with 3x10^7 viral particles of hAd5 intranasally (i.n.), and antigen-specific CD8+ T cells responses and antibody binding were evaluated. Antigen-specific T cell responses from the spleen of vaccinated mice were evaluated at day 8 post vaccination. (B) Representative flow plot of the intracellular interferon gamma production of CD8+T cells (gated on lymphocytes, CD8b+, and CD4-/CD19-) after ZIKV E294 peptide stimulation. (C) Percent of CD8+T cells secreting IFNγ in response to antigen-specific peptide stimulation with n = 6 per group. Asterisks indicate statistical significance * (p = 0.03), ** (p = 0.002), *** (p = 0.0002), and **** (p < 0.0001) as determined by Mann–Whitney test. (D) To determine the expression of ZIKV epitopes recognized after infection, ZIKV- and hAd5-ZKV-infected cells, and controls were evaluated by Western blot using ZIKV immune sera from C57Bl/6 mice. (E) Humoral responses were evaluated in the sera of immunized mice at day 21 post vaccination by ZIKV E protein binding with an n = 5 per group. Data are the cumulative results of two independent experiments, and significance was determined by student’s 2-tailed t test * (p = 0.03), ** (p = 0.002), *** (p = 0.0002), and **** (p < 0.0001).