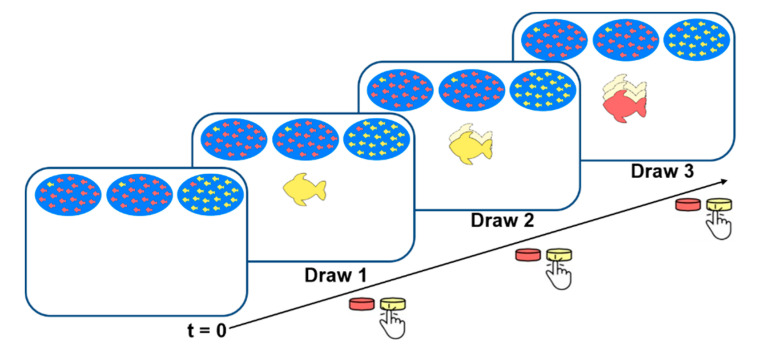
Figure 2.
An example of a sequence in the Bayesian oddball task [40]. Before stimulus presentation, the DL is twice as likely as a SL. In the following sequence, the subject sees a SLF at Draw 1, and indicates that they believe the SL to be more likely. A faded colour and broken outline indicate that this fish has been returned to the lake before the next fish is drawn. In this case, a SLF was presented at Draw 2, followed by a SL selection from the participant as indicated by the button press. Finally, a DLF fish is shown and the participant still believes the SL to be more likely.