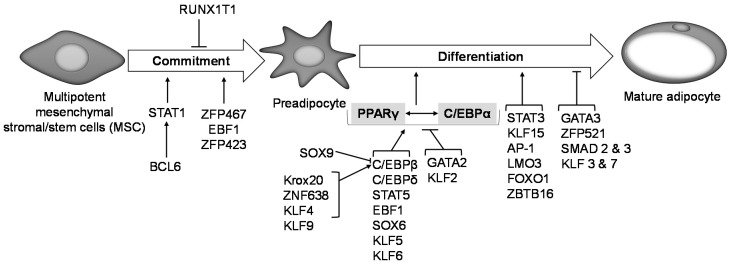
Figure 2.
Transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis. Transcription factors Zfp423, Zfp467, EBF1 and BCL6 promote preadipocyte commitment into the adipogenic lineage, while RUNX1T1 inhibits this process. Expression of PPARγ and C/EBPα is central to preadipocyte commitment and terminal differentiation, and several other transcription factors are known to regulate PPARγ and C/EBPα expression downstream. Activation of either PPARγ or C/EBPα transactivates the other. Krox20, ZNF638, KLF 4 and 9 activate C/EBPβ expression, which in turn activates PPARγ and thus promotes adipogenesis. SOX9 on the other hand binds to and suppresses C/EBPβ promoter activity and inhibits adipogenesis. KLF 5, 6 and 9, SOX6, EBF1, STAT5, C/EBPδ activate PPARγ expression thereby promoting adipogenesis. GATA2 and KLF2 inhibit PPARγ activation and suppress adipogenesis. STAT3, KLF15, AP-1, LMO3, FOXO1 and ZBTB16 are other transcription factors are reported to promote preadipocyte differentiation, while GATA3, ZFP521, SMAD 2 and 3, KLF 3 and 7 are reported to suppress it.