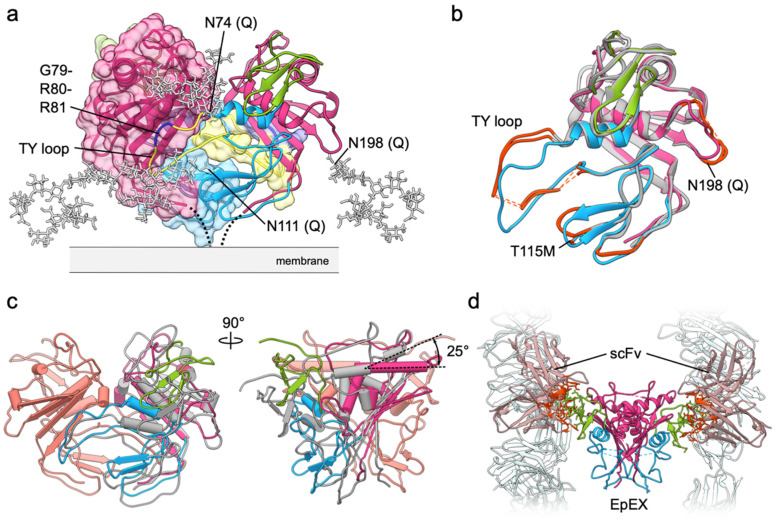
Figure 3.
EpEX cis-dimer. (a) The EpEX cis-dimer is mostly stabilized by interactions between TY loop (yellow) and concave β-sheet of the CD. Both subunits are shown as ribbons, with one covered by molecular surface color-coded in the same manner. Modeled high-mannose glycans are shown as gray sticks. The protease-sensitive site within TY loop is shown in dark blue. (b) Superposition of one EpEX subunit from EpEX-only structure (PDB 4MZV; color-coded by domains) and of the two subunits from the EpEX-scFv structure (PDB 6I07; gray). Significant structural differences are marked with orange-red. Missing segments in the EpEX-scFv structure are shown as dotted lines. (c) Superposition of the cis-dimers (calculated over one subunit) from the EpEX-only and scFv-EpEX structures. For the superposed subunits only one is shown (salmon), for the other subunit the color coding is the same as in (b). (d) In EpEX-scFv structure (PDB 6I07) the scFv molecules (light gray-pink) interact via several residues (orange-red) with NDs of the EpEX dimer (color coded by domains, ND in green). Few other symmetry-related scFv molecules in the crystal are shown in light gray.