Figure 3.
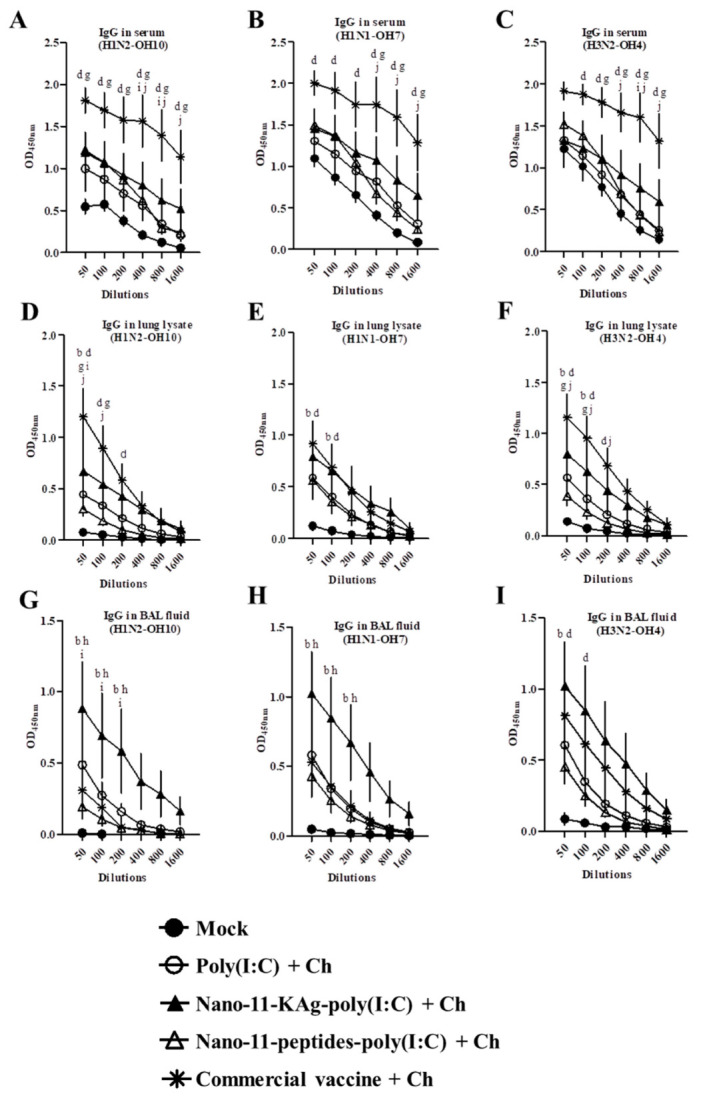
Commercial influenza vaccine augmented systemic IgG response and Nano-11-KAg-poly(I:C) vaccine in lower respiratory tract. Pigs were vaccinated twice with poly(I:C) adjuvanted Nano-11-based vaccines (containing H1N2-OH10 virus or 10 peptides) or commercial vaccine (containing H1N1, H1N2 and H3N2 viruses) and challenged (H1N1-OH7 virus) at 35 days post prime vaccination. Samples collected at day six post-challenge were used for IgG antibody analysis. The IgG antibody response in serum, lung lysate, and BAL fluid samples against (A,D,G) H1N2-OH10; (B,E,H) H1N1-OH7; and (C,F,I) H3N2-OH4 viruses were analyzed by ELISA. Data represent the mean value of four to five pigs ± SEM at all indicated dilutions. Statistical analysis was carried out using two-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni test. Each letter indicates the significant difference between the groups at the indicated dilution. b and d indicate the difference between mock group compared to Nano-11-KAg-poly(I:C) + Ch, and Commercial vaccine +Ch, respectively. g indicate the difference between poly(I:C) + Ch compared to Commercial vaccine +Ch. h and i indicate the difference between Nano-11-KAg-poly(I:C) + Ch compared to Nano-11-peptide-poly(I:C) + Ch and Commercial vaccine +Ch, respectively. j indicates difference between Nano-11-peptide-poly(I:C) + Ch) compared to Commercial vaccine +Ch. A p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Ch—Challenge.
