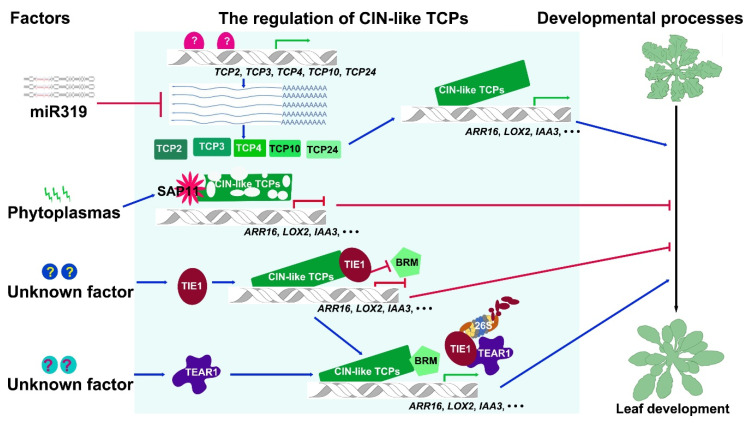
Figure 3.
An overview of the regulation mechanisms of CIN-like TCP transcription factors during leaf development. The external stimuli and internal factors are summarized at the left column. The schematic diagram includes the regulation mechanisms of CIN-like TCPs at the transcriptional level, at the post-transcriptional level, and at the protein level. The arrows directly pointing on the double helix symbols indicate transcriptional regulations. The arrows pointing to the proteins indicate the regulations of protein stabilities or antagonistic functions. The proteins related with the “26S” symbols indicate protein degradation through the ubiquitin-26S proteasome pathway. The blue arrows represent the positive regulation, and the red arrows with dash-headed ends indicate the negative regulation. The green arrows and red dash-headed ends at the double-helix icons indicates the activation and repression of gene expression, respectively. All the unknown factors are indicated with question marks. R:FR, red light: far red light ratio; YUCs, YUCCAs; LOX2, LIPOXYGENASE 2; SAP11, SECRETED AY-WB PROTEIN 11; ARR16, ARABIDOPSIS RESPONSE REGULATOR 16; IAA3, INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID INDUCIBLE 3; BRM, BRAHMA; TIE1, TCP INTERACTOR CONTAINING EAR MOTIF PROTEIN 1; TEAR1, TIE1-ASSOCIATED RING-TYPE E3 LIGASE 1.