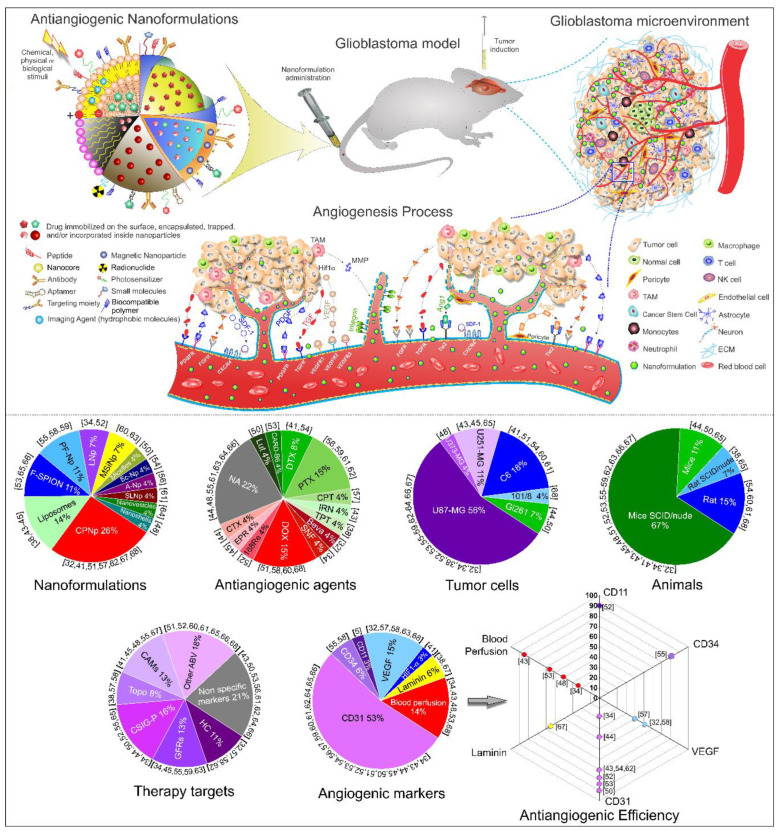
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of antiangiogenic nanoformulations for glioblastoma therapy from a pre-clinical approach and the angiogenic process in the tumor microenvironment and the pie charts of the main results found in the systematic review, as well as the quantification of antiangiogenic efficiency appointed by each study. Abbreviations—188Re: Rhenium-188; ABV: Angiogenic blood vessels; Ang1: Angiopoietin 1; Ang2: Angiopoietin 2; A-Np: Functionalized albumin nanoparticles; Beva: Bevacizumab; CAMs: Cell adhesion molecules; CARD: Nanoparticles with B6 loading three drugs ((CA4+AZO-ATRA+DOX+SPIONs)NPs); CPNp: Complex Polymeric Nanoparticles; CPT: Camptothecin; CSIG-P: Cell signaling pathways; CTX: Chlorotoxin; CXCR4: C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CD184); DOX: Doxorubicin; DTX: Docetaxel; ECM: Extracellular matrix; EPR: Epirubicin; FGF: Fibroblast growth factor; FGFR: FGF receptor; F-SPIONs: Functionalized SPIONs; GFRs: Growth factor receptors; HC: Hypoxic cascade; HIF1α: Hypoxia -inducible factor 1 α; IRN: Irinotecan; LNp: Lipid Nanocapsules; Lut: Luteolin; MMP: Metaloproteinase matrix; MSiNp: Multifunctional sílica based nanoparticles; NK cell: Natural killer cell; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor; PDGFR: PDGF Receptor; PF-Np: Peptide functional nanoparticles; PTX: Paclitaxel; SCID: Severe Combined Immunodeficiency; Sc-Np: Scalffold Nanoparticles; SDF-1: Stromal cell-derived factor 1; SLNp: Solid lipid nanoparticles; SNF: Sorafenib; TAM: Tumor-associated macrophage; TGF: Transforming growth factor; TGFR: TGF receptor; Tie 2: Ang1 and Ang2 receptors; Topo: Topoisomerase; TPT: Topotecan; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR1: VEGF Receptor type 1; VEGFR2: VEGF Receptor type 2; VEGFR3: VEGF Receptor type 3.