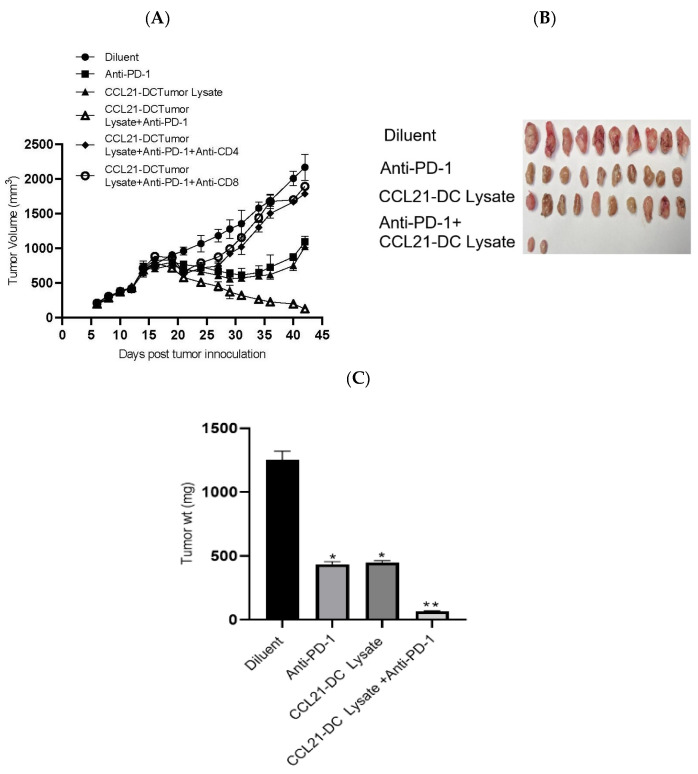
Figure 1.
K-RasG12Dp53null tumor cells (106) were inoculated in the supra scapular region of 129-E mice. Mice bearing 12-day established tumors were treated with (i) diluent, (ii) anti-PD-1, (iii) CCL21-DC lysate vaccine, (iv) CCL21-DC lysate vaccine plus anti-PD-1, (v) CCL21-DC lysate vaccine plus anti-PD-1 plus anti-CD4, and (vi) CCL21-DC lysate vaccine plus anti-PD-1 plus anti-CD8. In comparison to monotherapy, combined therapy was more effective at inhibiting tumor growth (A). Depletion of CD4 T or CD8 T cells abrogated antitumor activity of combined therapy (A). Combined therapy reduced the weight of tumors in comparison to monotherapy and control (B,C); ** p < 0.01 in comparison to diluent control, * p < 0.05 in comparison to monotherapy. Results are representative of an independent experiment. The experiment was repeated twice (n = 10 mice/group).