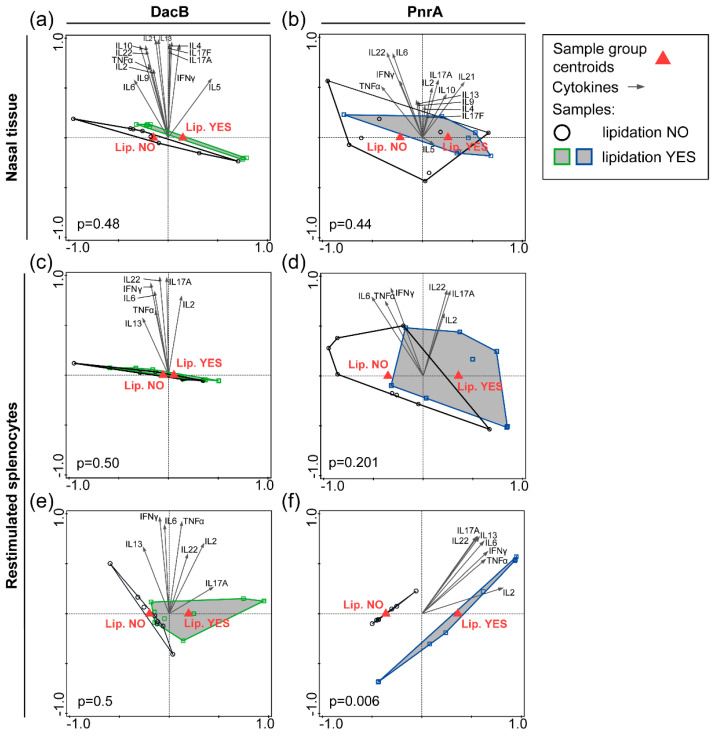
Figure 5.
Impact of lipidation on the cytokine response in the nasal tissue or in in vitro restimulated splenocytes of immunized and pneumococcal colonized mice. Nasal tissue of C57BL/6 mice (n = 8/group) that were intranasally immunized with lipidated or non-lipidated DacB (a) or PnrA (b) followed by an intranasal infection with S. pneumoniae three days prior to collection was analyzed. Cytokine levels in tissue homogenate were used for RDA to determine local lipidation-specific cytokine signatures for both proteins. Splenocytes were obtained from C57BL/6 mice (n = 4/group) that were intranasally (c,d) or subcutaneously (e,f) immunized followed by the pneumococcal infection. Cells were restimulated in vitro with lipidated proteins, matching the vaccination background, for 72 h. The cytokine levels were assessed and used for RDA irrespective of additional adjuvantation to evaluate systemic lipidation-specific cytokine signatures for DacB (c,e) and PnrA (d,f). Lipidation YES refers to mice vaccinated with lipidated proteins; and Lipidation NO refers to mice vaccinated with non-lipidated proteins. Arrows indicate individual cytokines, red triangles the sample group centroids, and squares/circles represent individual mice. p-values are shown; p < 0.05 is considered significant.