Table 1.
Overview of aptamer modifications discussed in this review. dZ—6-amino-5-nitro-3-(1′-β-D-2′-deoxyribofuranosyl)-2(1H)-pyridone; dP—2-amino-8-(1′-β-D-2′-deoxyribofuranosyl)-imidazo-[1,2-a]-1,3,5-triazin-4(8H)-one; Ds—7-(2-thienyl)-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine; Px—2-nitro-4-propynyl-pyrrole; 2′ F-ANA—2′-Fluoro arabino nucleic acid; LNA—locked nucleic acid; 5-IdU—5-iodo deoxyuridine; B—nucleobase.
| Modifications For Non-Covalent Target Binding | |||
| C5 modified nucleotides |
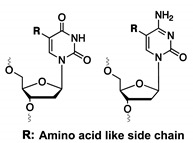
|
dZ-dP |
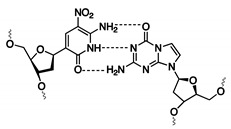
|
| dDs-dPx |
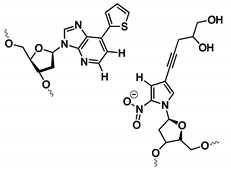
|
Thioaptamer |
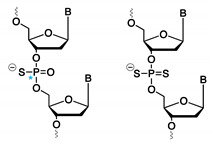
|
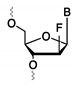
| 2′ F-ANA |
|
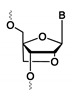
LNA |
|
| Modifications For Covalent Target Trapping | |||
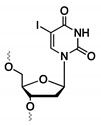
| 5′-IdU |
|
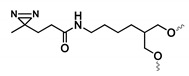
Diazirine |
|
| Aldehyde |
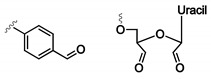
|
F-carboxyl |
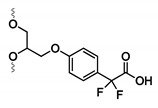
|
| Phenyl azide |
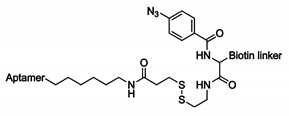
|
||
