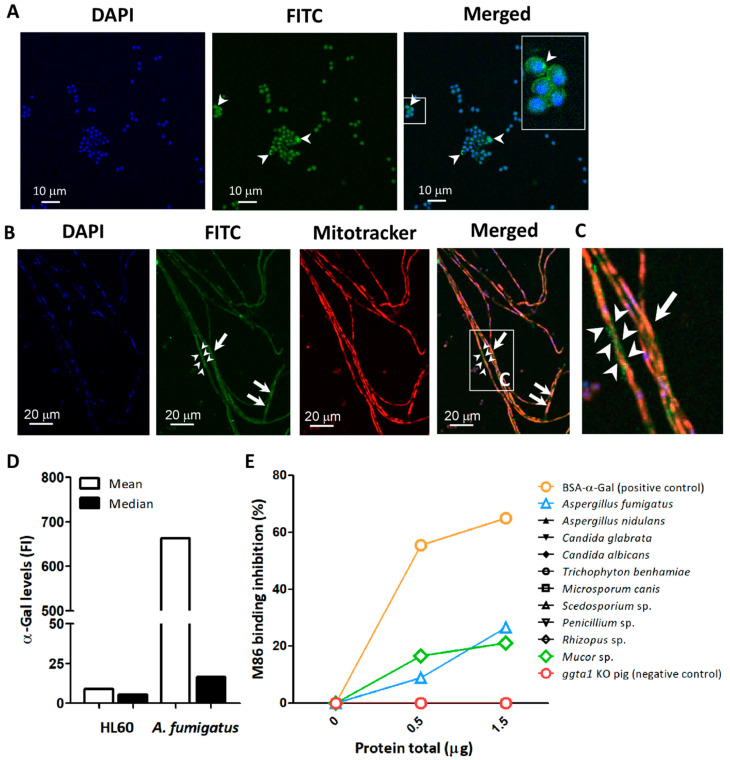
Figure 1.
Detection of α-Gal in A. fumigatus. The α-Gal-specific mAb M86 (primary Ab) was used to detect the production of α-Gal in A. fumigatus conidia (arrow heads) (A) and hyphae (B) by immunofluorescence. The mAb M86 was reactive to granular structures surrounding the hyphae (arrow heads) and the cytoplasm of hyphae cells (arrows) (B,C). Goat anti-mouse IgM-FITC was used as secondary Ab for detection of α-Gal (green). Cell nuclei and mitochondria were stained with DAPI (blue) (A,B) and Mitotracker (red) (B), respectively. α-Gal expression in conidia surface was measured by flow cytometry using M86 and Goat anti-mouse IgM-FITC. Mean and median fluorescence intensity (FI) values are presented. HL60 cells were used as a negative control (D). Presence of α-Gal glycan in protein extract of Ascomycota (i.e., A. fumigatus, A. nidulans, C. glabrata, C. albicans, M. canis, Penicillium sp., Scedosporium sp., and T. benhamiae) and Zygomycota (i.e., Mucor sp. and Rhizopus sp.) fungi was measured by inhibition ELISA assay (E).