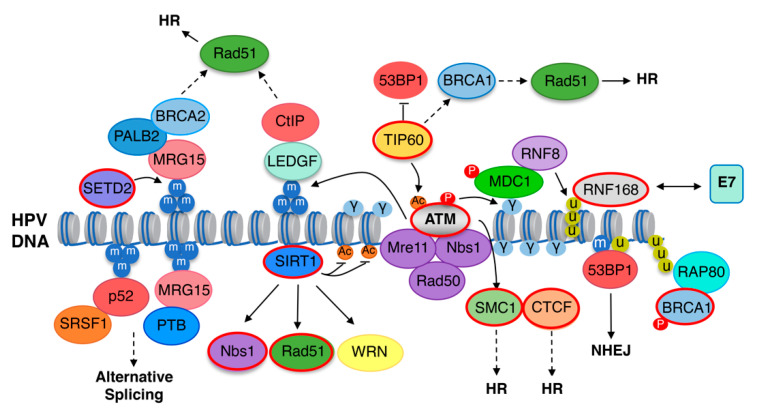
Figure 2.
DNA repair-induced epigenetic regulation of the HPV viral life cycle. DDR components shown to play a role in the HPV life cycle are highlighted in red. Upon DNA damage, DSBs can be recognized by the MRN complex (MRE11/Rad50/Nbs1), which, together with TIP60 acetyltransferase, promotes the activation of ATM through phosphorylation (depicted as P) and acetylation (depicted as Ac), respectively. Activated ATM acts as a primary signal to induce a signaling cascade through phosphorylation of histone H2AX on Ser139, forming γH2AX at DNA breaks (depicted as γ). γH2AX promotes the recruitment of various DDR effectors in a highly regulated manner at sites of damage via the binding of scaffolding protein MDC1. MDC1 also recruits the E3 ubiquitin ligase ring finger 8 (RNF8) to initiate K63-linked ubiquitin chains (depicted as U) on the histone linker H1, leading to the recruitment of E3 ubiquitin RNF168. RNF168 specifically catalyzes ubiquitination of H2A/H2AX on lysine 13/15 (H2AK13/15ub): a modification essential for accumulation of 53BP1 as well as the RAP80–BRCA1 complex. High-risk HPV E7 proteins directly interact with RNF168. TIP60 has been shown to block 53BP1 recruitment, which may in turn block NHEJ (non-homologous end-joining) and promote HR repair through the recruitment of BRAC1 and Rad51 to viral chromatin. SIRT1 recruits Nbs1 and Rad51 to HPV chromatin. SCM1 is recruited to HPV genomes in association with CTCF—both of which may contribute to productive replication through recruitment of HR factors. SETD2 mediates trimethylation of histone H3K36 (H3K36me3, depicted as m) to recruit effector proteins to regulate multiple cellular processes, including HR (homologous recombination) repair and alternative splicing, which are processes critical to completion of the HPV life cycle. SETD2-mediated H3K36me3 may facilitate HR repair through the recruitment of LEDGF-CtIP and MRG15-PALB2-BRAC1 to viral chromatin. Additionally, H3K36me3 regulates alternative splicing through recruitment of p52-SRSF1 and MRG15-PTB. ATM activity is also required for H3K36me3 maintenance on viral chromatin through an unknown mechanism. Dashed lines represent links that have not been tested experimentally.