Figure 2. ESCC and EAC PDO morphological characteristicsc.
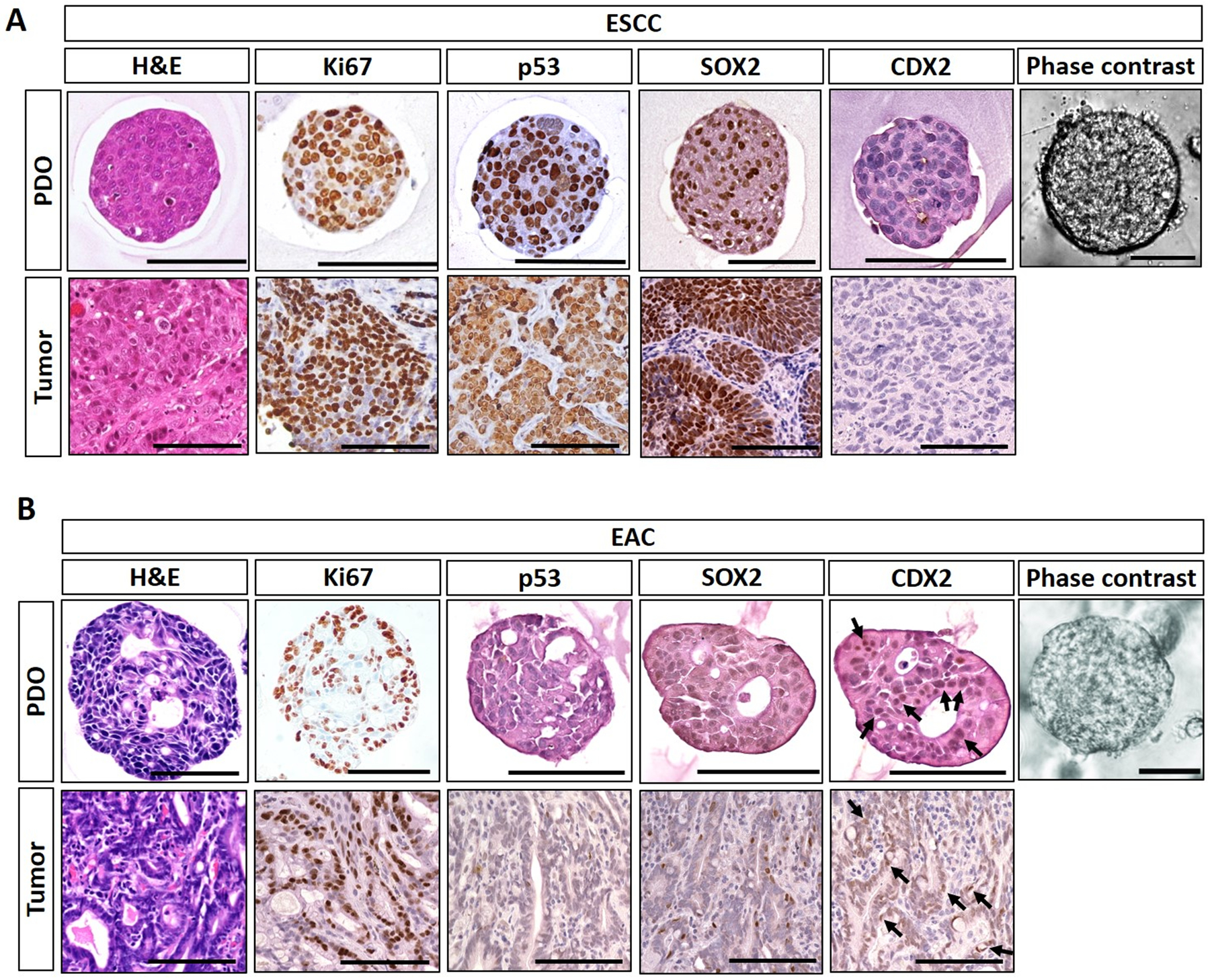
Representative ESCC (A) and EAC (B) PDO images under phase contrast microscope and histologic characterization of PDO as well as corresponding original primary tumor tissues by Hematoxylin-Eosin (H&E) staining and immunohistochemistry. ESCC PDO comprise poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma cells featuring increased cell proliferation (Ki67), stabilization of tumor suppressor TP53 protein, and overexpression of SOX2, an oncogene essential in ESCC. EAC PDO feature high chromatin density along with focal luminal formations reminiscent of glandular structures compatible with adenocarcinoma as corroborated by nuclear expression (arrows) of caudal type homeobox 2 protein (CDX2). Note that TP53 was negative in the representative EAC POD and original primary tumor. Cancer cells within PDO recapitulate those in original tumors. Scale bar, 100 μm.
