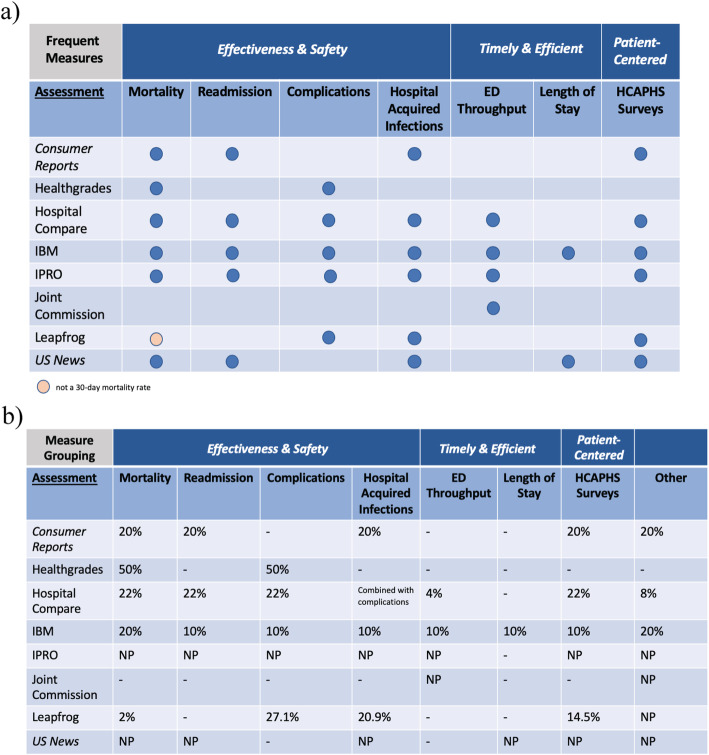
Fig. 3.
Frequent quality domain (a) measure overlaps and (b) comparison of their weights among assessments a) Abbreviations: ED, emergency department; HCAHPS, Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems. b) Descriptions of “Other” across assessments. Consumer Reports: Other, efficient use of imaging process measures; Hospital Compare: Other, 4% efficient use of imaging and 4% effectiveness of care process measures (e.g., patients assessed and given influenza vaccination; percentage of patients who left the ED before being seen; percentage of patients who came to the ED with stroke symptoms who received brain scan results within 45 minutes of arrival; percentage of patients receiving appropriate recommendation for follow-up screening colonoscopy; percentage of patients with history of polyps receiving follow-up colonoscopy in the appropriate timeframe; percent of mothers whose deliveries were scheduled too early (1-2 weeks early), when a scheduled delivery was not medically necessary; percentage of patients who received appropriate care for severe sepsis and septic shock; patients who developed a blood clot while in the hospital who did not get treatment that could have prevented it; percentage of patients receiving appropriate radiation therapy for cancer that has spread to the bone). IBM: Other, 10% operating profit margin (no mapping) and 10% adjusted inpatient expense per discharge for efficiency. IPRO: Other, weight not provided for timely and effective 1) stroke care (thrombolytic therapy, antithrombolytic therapy by end of hospital day 2, VTE prophylaxis, discharged on antithrombolytic therapy, anticoagulation therapy for atrial fibrillation/flutter, discharged on statin medication, stroke education), and 2) blood clot prevention and treatment (VTE prophylaxis, intensive care unit VTE prophylaxis, incidence of potentially preventable VTE, anticoagulation overlap therapy, unfractionated heparin with dosages/platelet count monitoring, warfarin therapy discharge instructions; safety, early elective delivery rates; efficiency, spending per Medicare beneficiary and health care costs; structural HIT measures and imaging for efficiency and safety; efficiency, population health and utilization costs; structural measures from county health rankings data on health factors and health outcomes related to preventive care for safety. Joint Commission: Other, weight NP for process measures. Timely and effective 1) stroke care (thrombolytic therapy, antithrombolytic therapy by end of hospital day 2, VTE prophylaxis, discharged on antithrombolytic therapy, anticoagulation therapy for atrial fibrillation/flutter, discharged on statin medication, stroke education; assessed for rehabilitation, VTE discharge instructions, and 2) blood clot prevention and treatment (VTE prophylaxis, intensive care unit VTE prophylaxis, incidence of potentially preventable VTE, anticoagulation overlap therapy, unfractionated heparin with dosages/platelet count monitoring, warfarin therapy discharge instructions; safety, early elective delivery rates; safety and effectiveness of antenatal steroids; safety and effectiveness for inpatient psychiatric services (admission screening, physical restraint, seclusion, and justification for multiple antipsychotic medications); safety and effectiveness of preventive care for influenza immunization, tobacco use (screening, treatment provided or offered, treatment provided or offered at discharge), hearing screening, alcohol use (screening, brief intervention provided or offered, or other drug use treatment provide or offered at discharge); effectiveness of exclusive breast milk feeding; surgical care effectiveness and safety of urinary catheter removal and antibiotics within one-hour before first surgical cut; safety and effectiveness, children’s asthma care, home management plan of care; and timely acute myocardial infarction measures (fibrinolytic therapy within 30 minutes and primary percutaneous coronary intervention received within 90 minutes). Leapfrog: Other, 23.1% safety practice process measures (leadership structures and systems; culture measurement, feedback, and intervention; identification and mitigation of risks and hazards; nursing workforce; hand hygiene) and 11.5% HIT (computerized physician order entry and bar code administration) safety, timeliness, and efficiency. Notably, the weights provided by Leapfrog only sum to 97.3% rather than 100%. US News: Other, weight NP for process measures on effectiveness (patient flu immunization and worker flu immunization) and safety (noninvasive ventilation and transfusion); outcome measures on patient-centeredness and safety (discharge to location other than patient’s home); structural safety measures related to information on board certifications and specialties, number of patients (volume), nurse staffing, number of intensivists, and transparency (reporting of performance). Abbreviations: ED, emergency department; HCAHPS, Hosptial Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems; HIT, health information technology; NP, not provided; VTE, venous thromboembolism; -, not an included measure