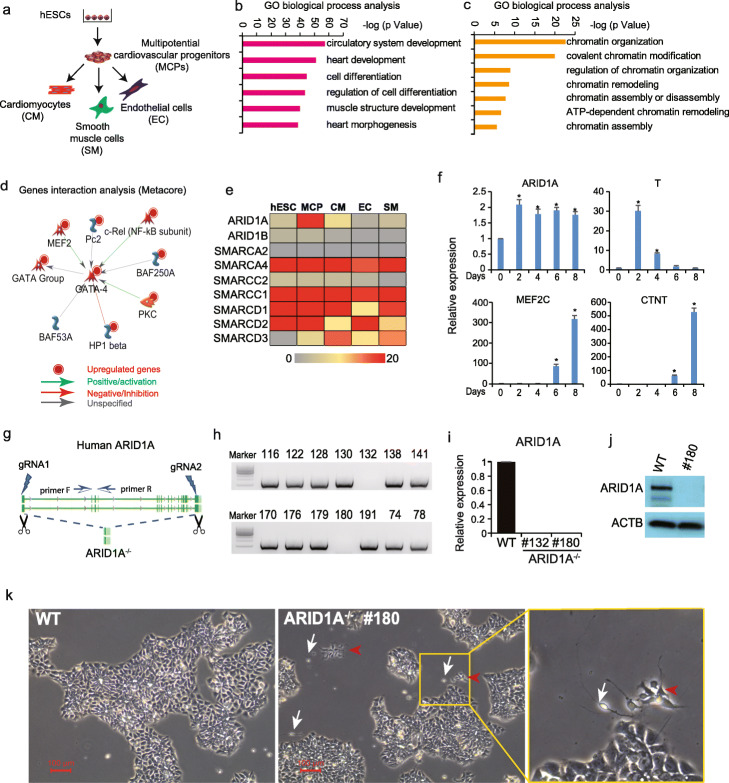
Fig. 1.
Loss-of-ARID1A induces spontaneous differentiation of hESCs. a Scheme for whole transcriptome sequencing of cardiovascular cell lineages derived from human embryonic stem cells (hESCs). b, c Gene Ontology (GO) biological process analysis of upregulated genes (MCP vs. hESCs) showing enriched heart development events (b) and epigenetic regulation events (c) during human cardiac development. d Interaction network analysis of SWI/SNF complex subunits and other cardiogenic genes by Metacore software. e Gene expression profiles of SWI/SNF subunits in different cardiovascular lineages by whole transcriptome sequencing. f Expression dynamics of ARID1A and key cardiac genes during cardiac differentiation of H9 hESCs. RNAs were collected every 2 days from day 0 to day 10 of cardiac differentiation. g Strategy for completely knocking out human ARID1A in H9 hESCs using CRISPR/Cas9. h PCR screening for ARID1A−/− hESC clones. i ARID1A mRNA expression detected by qRT-PCR. All bars are shown as mean ± SD. n = 3, *p < 0.05 (an unpaired two-tailed t test with Welch’s correction). j ARID1A protein expression levels detected by Western blot. k WT and ARID1A−/− hESCs were cultured in mTesR medium. ARID1A−/− hESCs displayed small clusters of differentiated cells (red arrow heads and white arrows indicate two different cell types). All functional analysis and gene interaction network analyses were done by Metacore (Clarivate Analytics)