Figure 2.
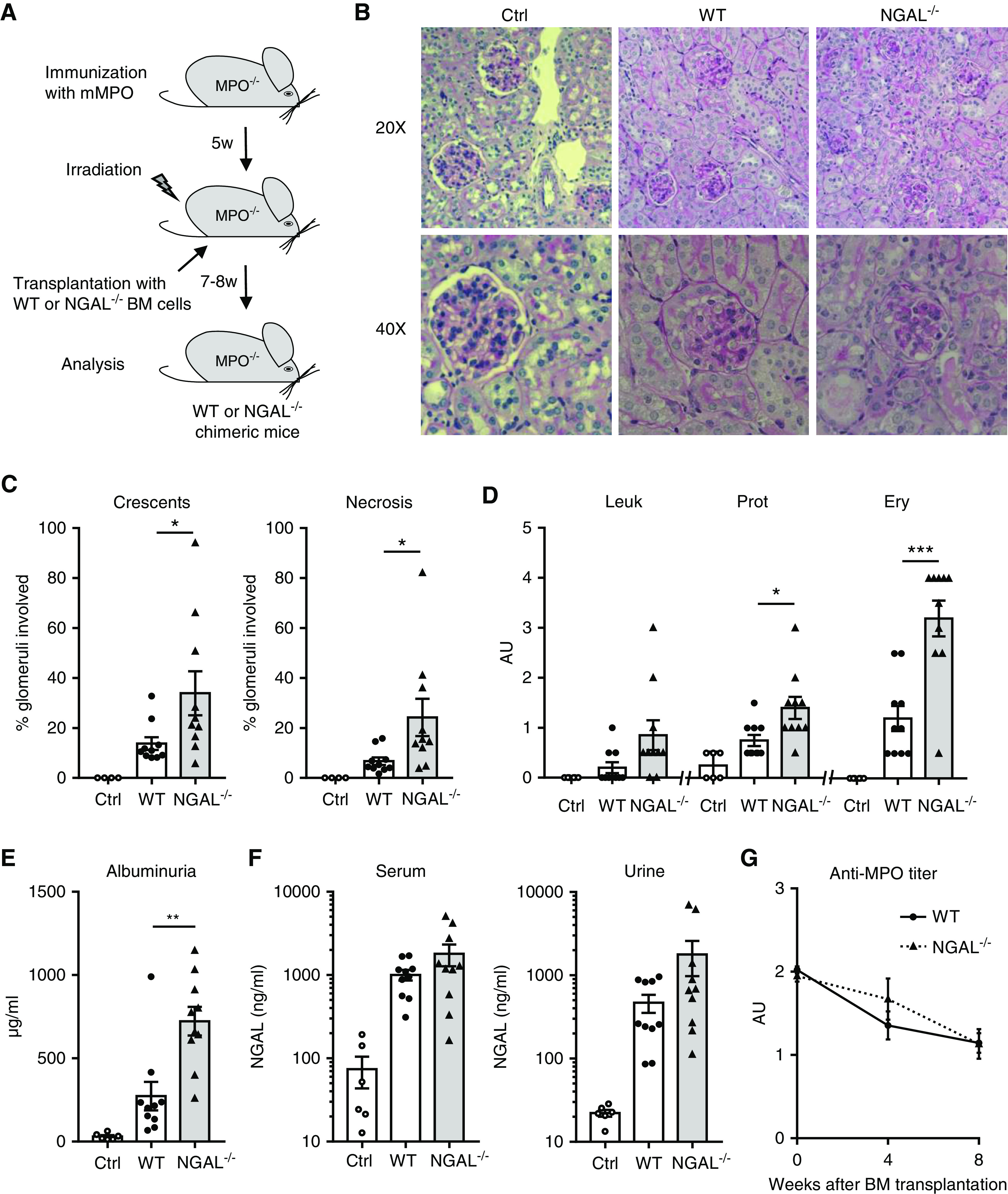
NGAL−/− chimeric mice develop more severe anti-MPO–induced NCGN, but show similar NGAL levels in serum and urine compared with WT mice. (A) Experimental scheme depicting the induction of NCGN in MPO-deficient (MPO−/−) mice immunized with murine MPO (mMPO) that were subsequently irradiated and transplanted with either WT or NGAL-deficient (NGAL−/−) BM cells. All chimeric mice were analyzed 7–8 weeks after transplantation. (B) NGAL−/− chimeric mice developed more severe NCGN than WT chimeric mice with (C) higher percentage of crescents and necrosis. Shown are representative images of kidney sections stained with Periodic acid–Schiff at low (20×) and high (40×) magnification and quantitative analyses of glomeruli with crescents and necrosis. (D) Urine analysis reveals more erythrocyturia (Ery) and proteinuria (Prot) in NGAL−/− chimeric mice by dipstick and (E) higher albuminuria by ELISA, whereas (F) serum and urinary NGAL levels were similar in WT and NGAL−/− chimeric mice by ELISA. (G) Anti-MPO titer determined by ELISA was similar in WT and NGAL−/− chimeric mice. Ctrl, control; Leuk, leukocyturia. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.
