FIGURE 1.
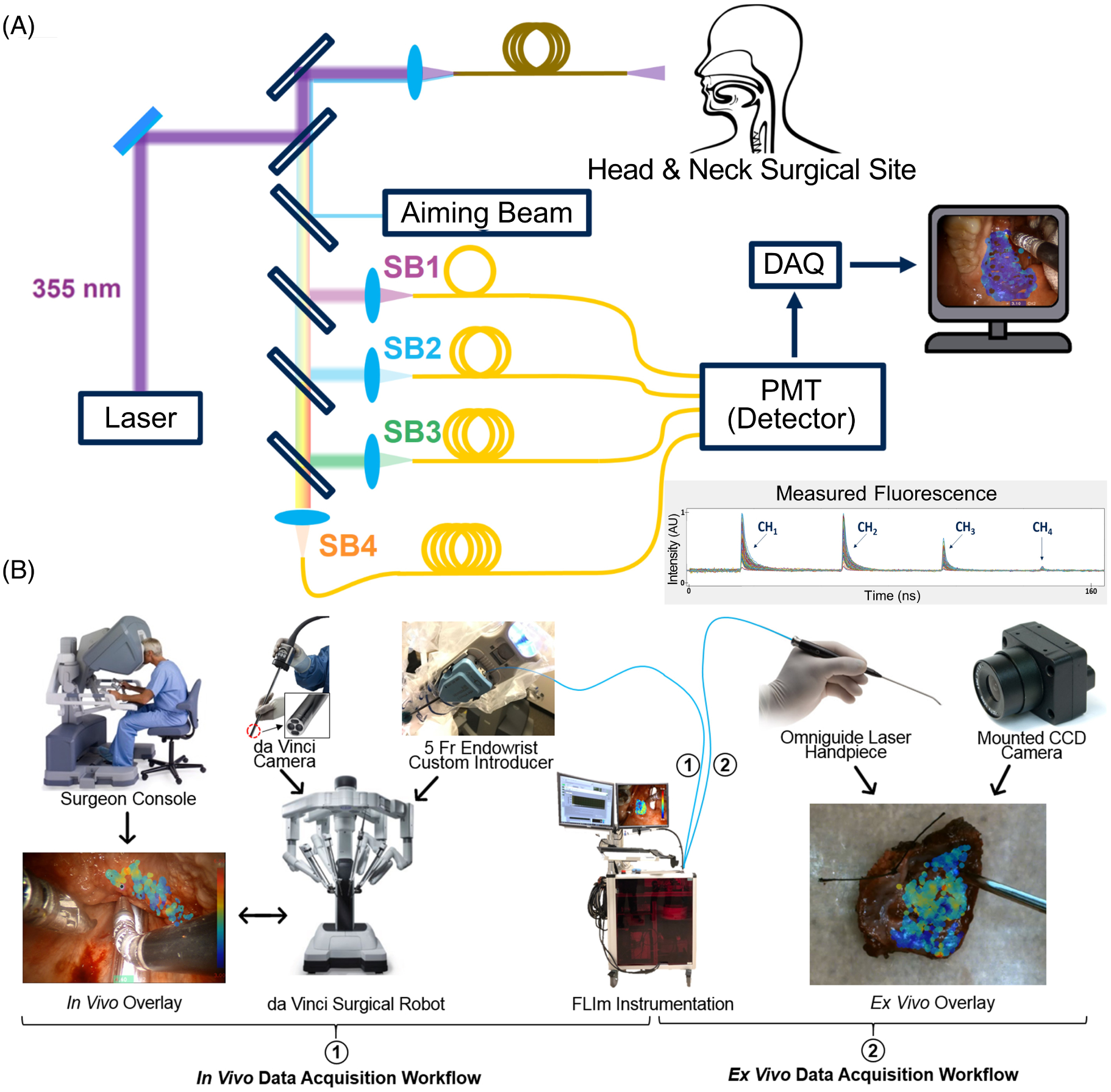
Overview of the fluorescence lifetime imaging (FLIm) instrumentation and workflow in the operating room. (A) Schematic of the custom-built FLIm system, featuring the excitation beam to generate autofluorescence, the aiming beam to spatially coregister data, and the four spectral channels to resolve fluorescence lifetime and spectral intensity. Also illustrated is an example of the measured fluorescence waveforms output from the four time-delayed spectral channels; the method for the detailed calculation of fluorescence lifetime and spectral intensities for each spectral channel is described by Liu et al. [27]. (B) Integration of the FLIm system with the da Vinci robotic system in the OR workflow: (1) represents the in vivo workflow for both pre-resection and post-resection (cavity) analysis where the da Vinci surgical system (including the integrated camera) was leveraged to collect measurements, and (2) represents the ex vivo workflow used for resected specimen pathology assessments where an Omniguide Laser Handpiece was used to perform a hand-held scan visualized by a mounted camera. The surgeon console and da Vinci system images are adapted with permission from Intuitive Surgical Inc
