Figure 1. AcrIIA1 Induces Cas9 Degradation in Listeria.
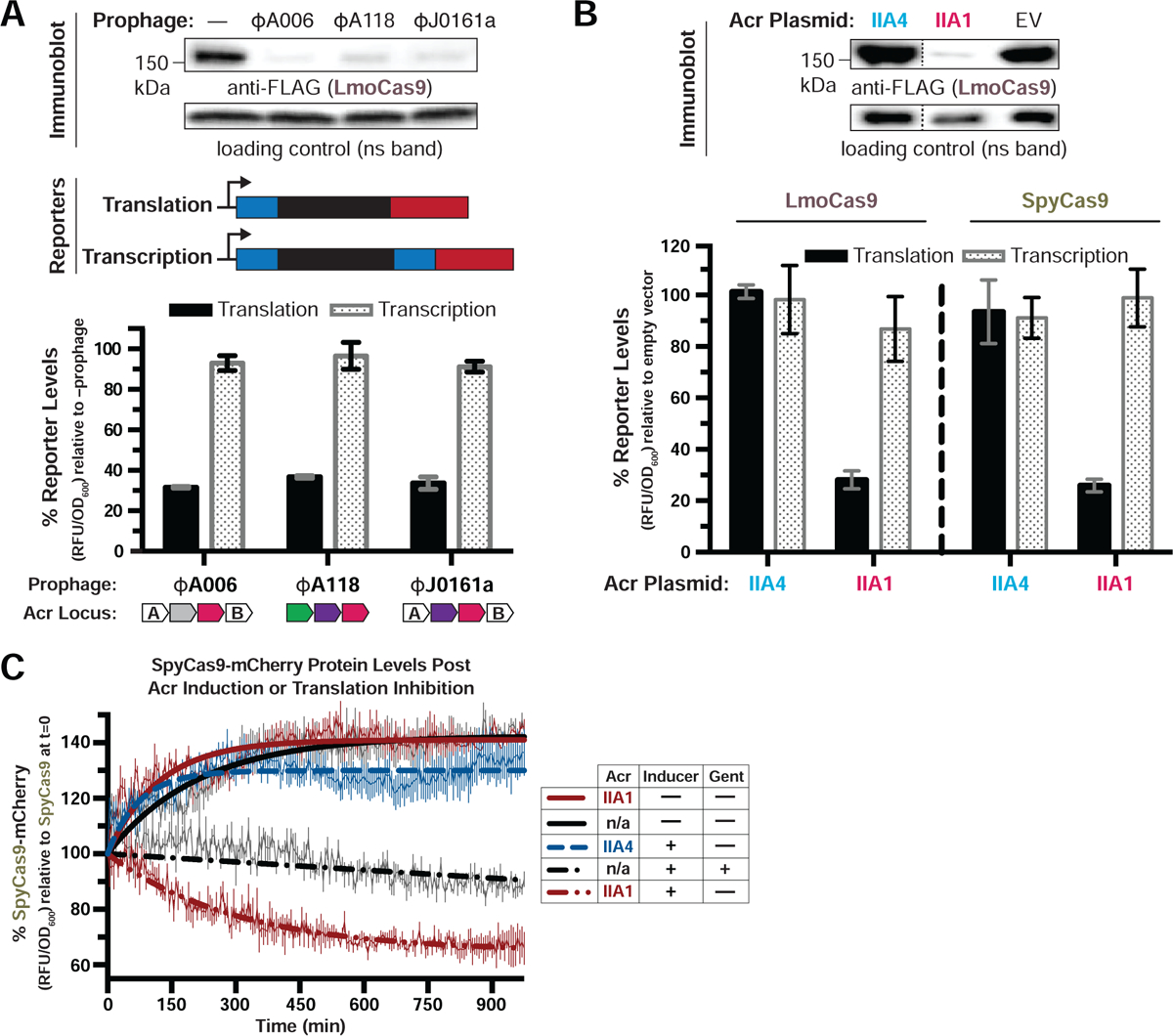
(A-B) Immunoblots detecting FLAG-tagged LmoCas9 protein and a non-specific (ns) protein loading control in Listeria monocytogenes strain 10403s (Lmo10403s) lysogenized with the indicated wild-type prophages (A, top) or Lmo10403s containing Acr-expressing plasmids (B, top). Dashed lines indicate where intervening lanes were removed for clarity (B, top). Representative blots of at least three biological replicates are shown (A and B). Schematics of translational and transcriptional reporters used to measure Lmo or Spy Cas9 protein and mRNA levels in Lmo10403s (A, middle). Cas9 translational (black bars) and transcriptional (gray shaded bars) reporter measurements reflect the mean percentage mCherry relative fluorescence units (RFU/OD600) in the indicated lysogens (A, bottom) or strains with Acr-expressing plasmids (B, bottom) relative to the control strain lacking a prophage (−prophage) (A, bottom) or containing an empty vector (B, bottom). Error bars represent the mean ± SD of at least three biological replicates. (C) SpyCas9-mCherry protein levels post Acr induction or translation inhibition. Lmo10403s expressing SpyCas9-mCherry from the constitutively active pHyper promoter and AcrIIA1 or AcrIIA4 from an inducible promoter were grown to mid-log phase and treated with 100 mM rhamnose to induce Acr expression (dashed lines) or 100 mM glycerol as a neutral carbon source control (solid lines) and 5 μg/mL gentamicin (Gent) to inhibit translation (+) or water (−) as a control. SpyCas9-mCherry protein measurements reflect the mean percentage fluorescence (RFU/OD600) relative to the SpyCas9-mCherry levels at the time translation inhibition was initiated (0 min). Error bars (vertical lines) represent the mean ± SD of at least three biological replicates. Data were fitted by nonlinear regression to generate best-fit decay curves. See Figure S1C for additional controls and S1B for data showing tight repression of the pRha promoter under non-inducing conditions. Note: Lmo doubling time is significantly slower in LB media containing glycerol and/or rhamnose carbon sources (Fieseler et al., 2012).
