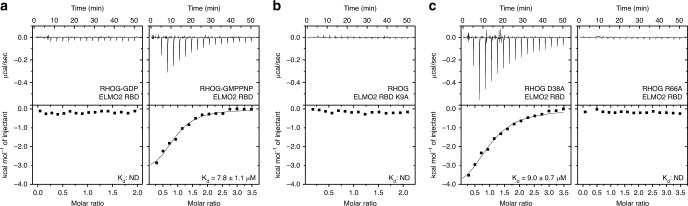
Fig. 5. Mutations of the RHOG–ELMO2RBD interface disrupts interactions.
ITC binding assay for (a) Wild-type RHOG in the inactive GDP-bound state (left) or active GTP-bound state (right) with wild-type ELMO2RBD; (b) K9A mutant of ELMO2RBD with wild-type RHOG; and (c) D38A and R66A mutants of activated RHOG with wild-type ELMO2RBD. For ITC assays showing no binding, the Kd was not determined (ND). The positions of these residues are shown in Fig. 4c. The experiments were performed independently three times with similar results.