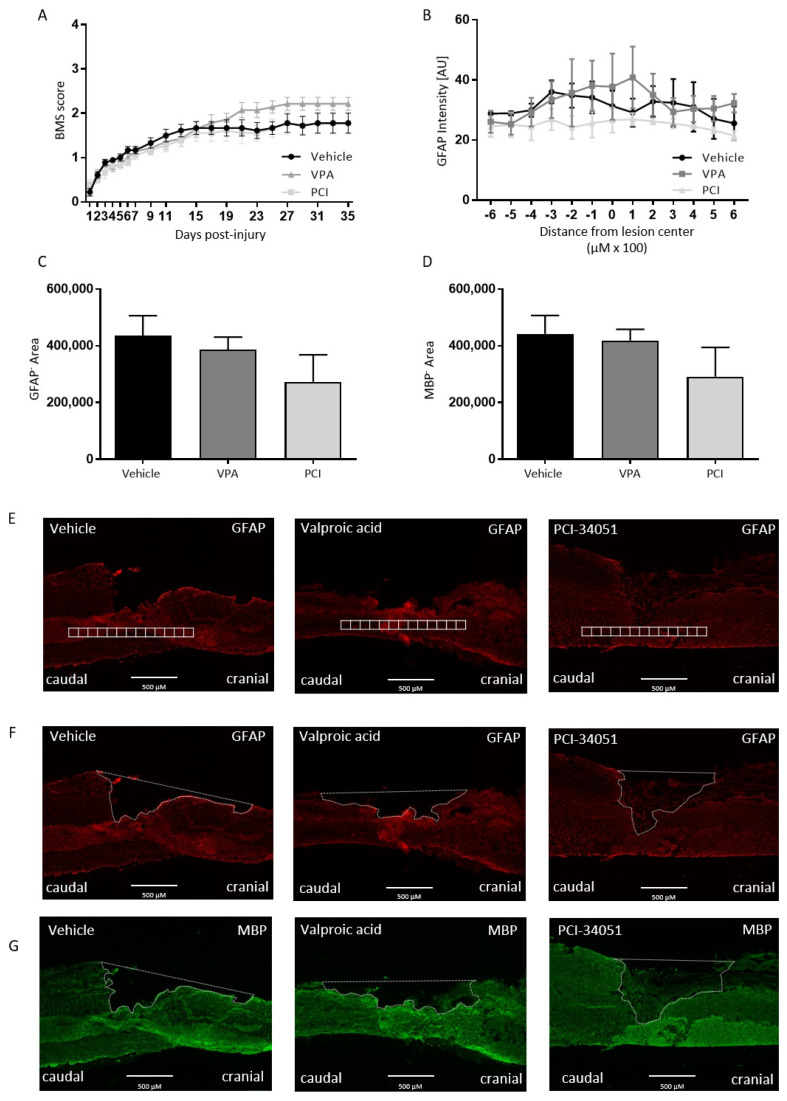
Figure 3.
PCI-34051 and VPA have no effect on functional recovery, lesion size, or demyelinated area after SCI. BALB/c mice were subjected to a T-cut hemisection SCI. For the first 5 days, the mice were injected i.p. with VPA (250 mg/kg), PCI-34051 (20 mg/kg), or vehicle. (A) Recovery of hindlimb motor function was determined using the Basso Mouse Scale (BMS). Treatment with PCI-34051 has no effect on functional recovery after SCI. In addition, VPA showed no effect on functional recovery. Sections were labelled for GFAP (lesion size, astrogliosis) and MBP (demyelinated area). (B–D) No changes were observed for lesion size, astrogliosis, and demyelinated area when VPA or PCI-34051 were administered. (E–G) Representative images show the method of quantification: GFAP expression was quantified by intensity analysis within rectangular areas of 100 µm × 100 µm, extending 600 µm cranial to 600 µm caudal from the lesion epicentre. GFAP-area and MBP-area are delineated to evaluate the lesion size and demyelinated area. Data are represented as means ± SEM, n = 7–9 mice/group for BMS and n = 3 mice/group for the histological analyses. SCI: spinal cord injury; BMS: Basso mouse scale; GFAP: glial fibrillary protein; MBP: myelin basic protein; VPA: valproic acid; PCI: PCI-34051.