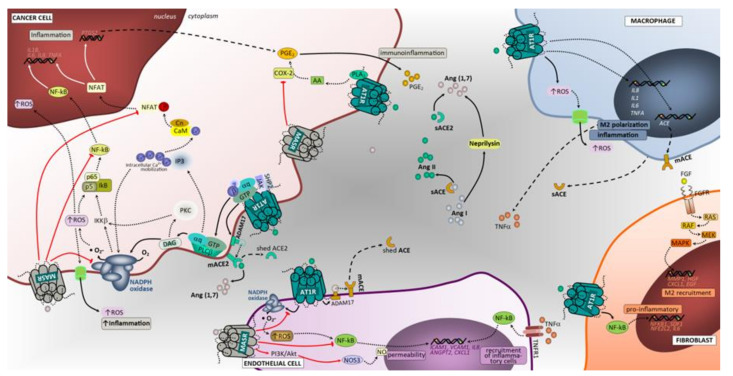
Figure 4.
Angiotensin-associated immunoinflammatory pathways in lung tumor microenvironment. Extracellular proteins of the RAS, ligands (Ang I, Ang II and Ang 1,7) and enzymes (ACE, ACE2 and neprilysin), are represented with distinct colors in the tumor microenvironment. The expression and cleavage of ACE and ACE2 are represented in tumor and endothelial cells, showing the AT1R signaling-associated activation of ADAM17 that cleaves the ectodomain of mACE and mACE2 shedding the enzymes into sACE and sACE2. The Ang II/AT1R-mediated direct intracellular signaling is represented with full black arrows as a first step after AT1R triggering in the cascade. The subsequent steps of signaling cascades are depicted, up to moving towards intranuclear space, using dashed black arrows. Intranuclear signaling from these pathways mainly results in transcriptional regulatory effects and is represented by full white arrows. The Ang II/AT2R and Ang (1,7)/MasR-mediated counter-regulatory mechanisms are depicted using black arrows and when adequate the suppressive step is represented by blunt-ended red arrows. In cancer cells, upon binding of Ang II to AT1R, a pleiotropic downstream signaling cascade is triggered, ultimately causing, either directly or indirectly inflammation immune cells recruitment. Activated AT1R triggers potent oxidant signaling through NADPH complex, which is involved in inflammation and angiogenesis. Other intracellular cascades mediated by Ang II/AT1R include the activation of PLA2/AA/COX-2/PGE2 signaling. The Ang (1,7)/MasR activation elicits downstream signaling through PI3K/Akt/NOS3 or NOS1 to produce NO that inhibits NFAT transcriptional regulation that reduces inflammation. Notably, this pathway blocks the NF-kB molecule formation thereby impacting inflammation. In addition, the inhibitory effect over COX-2 significantly impact inflammation. Macrophages, endothelial cells and fibroblasts are important components of the tumor microenvironment and capable of generating and expressing RAS components. These cells, beyond their functional ligands and receptors that are altered in tumor microenvironment, and reflect the crosstalk between all cell constituents, also use the RAS signaling pathway (mostly AT1, but also MasR in endothelial cells) to yield functional characteristics that ultimately may favor the cell itself and enhance tumor growth and aggressiveness. PLA2, phospholipase A2; PTP, protein tyrosine phosphatase; PP2A, Protein phosphatase 2; IKKB, Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta; CARMA3, CARD recruited membrane associated protein 3; MALT1, Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1; BCL-10, B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 10; c-SRC, cellular Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase; SHP2, Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-2; AA, arachidonic acid; COX-2, cyclooxygenase 2; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; IL1, interleukin 1; TNFA, tumor necrosis factor; Ang I, angiotensin I; Ang II, angiotensin II; GTP, guanosine triphosphate; EGF, epidermal growth factor; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; ANGPT2, angiopoietin 2; ICAM1, Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1; VCAM1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; CXCL1, The chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1; IL8, interleukin 8; NF-kB, Nuclear Factor-kappa B; NFKB1, Nuclear Factor-kappa B Subunit 1; IL6, interleukin 6; NFE2L2, Nuclear Factor, Erythroid 2 Like 2; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; RAS, oncogene protein p21; ROS, reactive oxygen species; NOS3, nitric oxide synthase 3 endothelial; NOS1, nitric oxide synthase 1 neuronal; Cas9, caspase 9; Cas3, caspase 3; ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; PLCγ/PKC, phospholipase C gamma/protein kinase C; PI3K/Akt, phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B; TNFR1, tumor necrosis factor receptor 1; c-Raf, kinase Raf-1; MEK1/2, mitogen activated protein kinase kinase; HIF1α, hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha; NO, nitric oxide; RhoA, Ras homolog family member A; IP3, inositol trisphosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol; M2, macrophage polarized towards M2; ADAM17, Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 17; p38/MAPK, protein 38/mitogen activated protein kinase; AT1R, angiotensin receptor 1; AT2R, angiotensin receptor 2; MASR, G-protein coupled Mas receptor; VEGFA, vascular endothelial growth factor A; NADPH, reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; mACE, membrane angiotensin converting enzyme; sACE, soluble angiotensin converting enzyme; mACE2, membrane angiotensin converting enzyme 2; sACE2, soluble angiotensin converting enzyme 2; PDGFRβ, platelet derived growth factor receptor beta; VEGFR1, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1; VEGFR2, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2; TGFα, transforming growth factor alpha; Ang (1,7), angiotensin 1,7; PLCβ, phospholipase C beta; FAK, Focal adhesion kinase; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; PDGF, platelet derived growth factor.