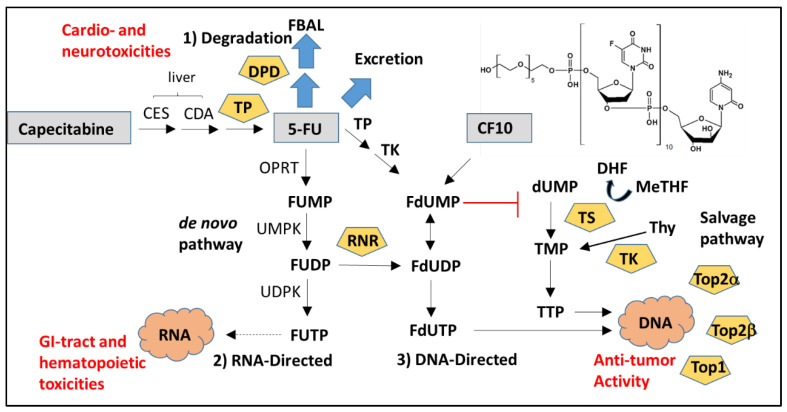
Figure 1.
Overview of fluoropyrimidine metabolism. Fluoropyrimidines exert biological effects thru three types of metabolites: (1) Degradation; (2) RNA-directed; and (3) DNA-directed. Most 5-FU is either degraded or excreted intact and degradation metabolites contribute to cardio- and neurotoxicities. RNA-directed metabolites cause GI-tract and hematopoietic toxicities and contribute to immunosuppression. DNA-directed metabolites are responsible for the anti-cancer activity of fluoropyrimidines. Fluoropyrimidine polymers (e.g., CF10) are more efficiently converted to DNA-directed metabolites and may reduce the immunosuppressive and pro-inflammatory effects of 5-FU.