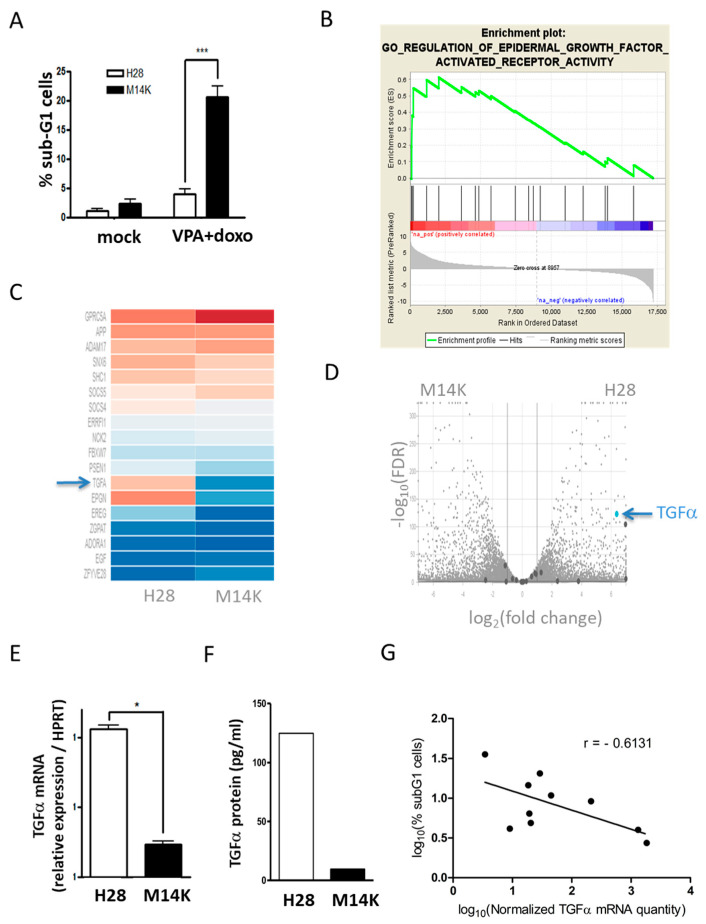
Figure 1.
The sensitivity of mesothelioma (MPM) cells to valproic acid (VPA)-doxorubicin chemotherapy negatively correlates with expression of TGFα. (A) H28 and M14K mesothelioma cells were treated for 24 h with VPA (2 mM) and doxorubicin (100 nM). Apoptotic DNA fragmentation was evaluated by flow cytometry after ethanol fixation and propidium iodide labeling. Data (% of sub-G1 cells) are means ± standard deviations (SD) of three independent experiments. p-value < 0.001 (***) was obtained by the independent Student’s t test. (B) RNA sequencing of H28 and M14K cells. Enrichment plot of epidermal growth factor activated receptor (EGFR) activity gene set determined by gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA). (C) Hierarchical heat map of genes belonging to GO regulation of EGFR activity gene set. (D) Volcano plot based on log2 (fold change) and −log10 (false discovery rate, FDR). (E) The difference in TGFα transcription was confirmed by RT-qPCR in H28 and M14K cells. The HPRT housekeeping gene was used as an endogenous control in order to normalize TGFα expression. RT-qPCR data are represented as means ± SD, and statistical significance was calculated using the Mann-Whitney U test (* p-value < 0.05). (F) Quantification of TGFα protein by ELISA. (G) A correlation test (Pearson) was performed between the log10-transformed data of normalized TGFα expression and the levels of apoptosis induced by VPA-doxorubicin in 10 mesothelioma cell lines (M14K, M38K, MSTO-211H, NCI-H2452, H28, SPC111, SPC212, ZL34, ZL5 and ZL55). Apoptosis was measured by quantifying the proportion of sub-G1 cells by flow cytometry. The results are means of three independent experiments, and the Pearson correlation coefficient (r) is represented on the graph (p-value = 0.0594).