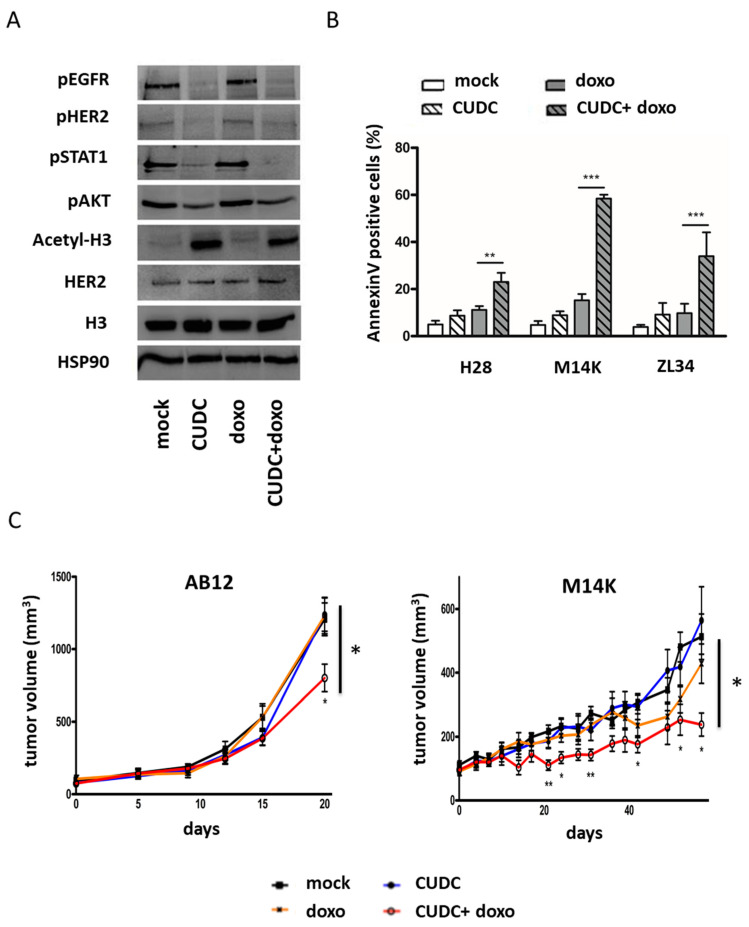
Figure 4.
An inhibitor targeting EGFR/HER2 and HDAC synergizes with doxorubicin to induce apoptosis and inhibit tumor growth. (A) Representative immunoblotting of H28 cell lysates evaluating the phosphorylation of EGFR, STAT1, AKT and HER2 as well as the acetylation of histone H3 in response to doxorubicin and/or the EGFR/HER2/HDAC inhibitor (CUDC-101 at 1 µM). Heat-shock protein 90 (HSP90) was used as a loading control. (B) The apoptosis induced by CUDC-101 (1 µM) and/or doxorubicin (100 nM) was quantified by an Annexin V assay in three mesothelioma cell lines (H28, M14K and ZL34). Data represent the means ± SD of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. ** p-value < 0.01; *** p-value < 0.001. (C) Tumor growth of AB12 (murine) and M14K (human) mesothelioma cells was evaluated after subcutaneous injection in BALB/c and NOD-SCID mice, respectively. Mice were treated intraperitoneally with mock (30% Captisol), doxorubicin (0.5 mg/kg once a week) or/and CUDC-101 (100 mg/kg twice a week). The tumor volume was measured at regular intervals. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used at the different time points to evaluate the statistical significance (* p-value < 0.05; ** p-value < 0.01) between the different treatment conditions (six mice per group).