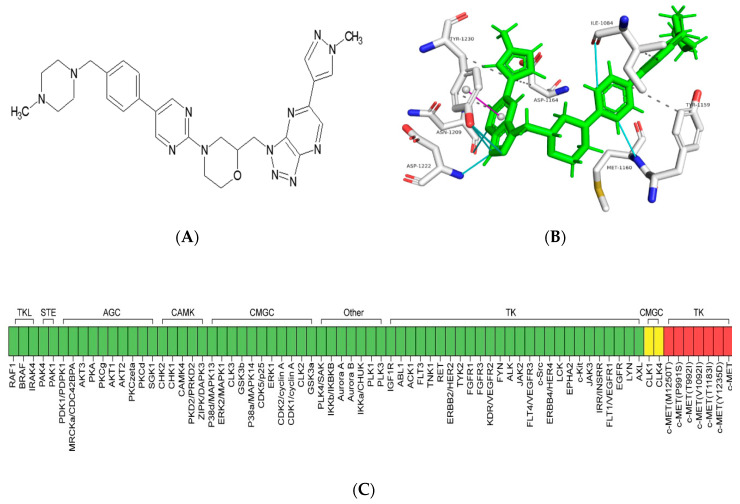
Figure 1.
Characteristics of ABN401 as a highly potent and selective c-MET inhibitor. (A) Chemical structure of ABN401. (B) The binding modes of ABN401 determined using molecular docking simulation. ABN401 in the binding site of the c-MET kinase domain (white colored) is indicated with a line-stick model. The heavy atoms of nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur are colored in blue, red, and yellow, respectively. The interactions between protein and inhibitors are shown, including hydrophobic interactions (gray colored), hydrogen bonds (cyan colored), and pi-stacking (magenta colored). (C) Kinase selectivity profiling of ABN401 in a panel of 571 kinases. TKL: Tyrosine kinase-like, STE: Homologs of yeast Sterile 7, 11, 20 kinases, AGC: Containing PKA, PKG, PKC families, CAMK: Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase, CMGC: Containing CDK, MAPK, GSK3, CLK families, TK: Tyrosine kinase.